Impact of Covid-19 on the Hospitality Industry
Impact of Covid-19 on the Financial and Economic Operational Scenario of Hospitality Industry: A comparative study with Pre Covid-19 Era in the United Kingdom
Executive Summary
The following report has performed a research study that focused on determining the impact of Covid-19 on the financial and economic operational scope of the hospitality industry and further compare with business situation before the virus outbreak took place. The study has been conducted in the UK that is largely known for a highly prosperous hospitality operational sector. For this purpose, secondary quantitative method has been used for the analysis of data. The data has been collected using the Bloomberg website. The data findings stated that the economic and business environment of the hospitality sector of the UK is experiencing severe financial turmoil.
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank my parent and friends who have helped me in keeping myself motivated all throughout the research work. Also, I would like to express my sincere gratitude to my guide, without whose help and coordination it would have been impossible for me to become successful in conducting the research work.
Table of Contents
Chapter 2: Literature Review.. 9
2.3 Impact of Covid-19 on Financial and Economic Operational Environment 9
2.3.1 Financial Business Scenario. 10
2.3.2 Economic Business Scenario. 12
2.4 Pre Covid-19 Operational Scenario. 14
2.4.1 Financial Business Environment 14
2.4.2 Economic Business Environment 15
Chapter 3: Research Methodology. 17
3.10 Ethical Considerations. 21
Chapter 4: Data Findings, Analysis and Discussion. 22
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Future Implications. 30
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background
The high degree of fragmentation in the hospitality industry of the UK due to the presence of a large number of small-scale business plays a critical role in terms of enriching its financial health largely. The financial capability of the tourism industry and its contribution to the country’s government resulted in providing funds for promoting hospitality service operations to both national and international marketplaces (Jones, Hillier and Comfort, 2016). As a result, the organisations involved in the industrial operations experienced an unprecedented growth rate followed by immense enrichment of the UK economy too. The industry successfully procured wide range of financial investment from foreign investors, due to the widespread operational prospects offered by the hospitality industry of the country (Mok, Sparks and Kadampully, 2013).
The hospitality service industry contributes to about 5% of the national gross domestic product (GDP) of the country and also accounts for about 10% of its total employment rate too. The primary tourism market for the UK hospitality sectors are the major European nations like Germany, Italy, Spain, France, Belgium, Ireland, Australia and the US (Hospitality Net, 2020). Each of these source markets comprises of about more than 60% of the total inbound visitors to the country. Furthermore, it is to be noted that the nationalities of China and Canada occupies the top position when it comes to expenditure on hospitality industry. Based on this fact, it can be largely said that the hospitality industry of the UK was highly prosperous, contributing to the economic growth rate of the country before the global pandemic took place.
The outbreak of Covid-19 is considered to cause immense economic and financial turmoil of the hospitality industry due to the closedown of thousands of service providers. The new set of operational restrictions developed by government due to virus outbreak is identified as one of the primary factors underlying the shutdown of firms. It is due to the regulation imposed by the government to avid social contact among people and thereby urging people to stay away from restaurants, pubs and hotels (BBC, 2020). The global pandemic is considered to be catastrophic for hospitality businesses as well as large number of jobs associated with it. The new hospitality operational regulations further resulted in many businesses to declare permanent shutdown followed by causing a massive increase of unemployment rate in the industry.
1.2 Problem Statement
The macroeconomic business environment plays an important role as a means of determining the growth prospect and development scope of organisations operating in the hospitality sector (Global Data, 2020). It is due to the strong dependence of the macroeconomic factors on the business prospects. The favourable operational scenarios resulted in the hospitality business sector of the UK to experience widespread economic and financial prospects. The presence of a large number of organisations played a significant role in terms of catering to the diversified hospitality needs of the customers. The tourism industry of the UK is well knownand each of organisations have experienced widespread sales revenue based on their operational scope and capabilities. However, the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic altered the business scope of the industry largely. A 97% decline in the sales have been witnessedby the organisations experiencing immense uncertainty relating to how the business operations should be run further (Werner et al., 2020). Moreover, the lockdown and travel restrictions resulted in altering the operational process and further reduces the employment opportunities within the sector. A significant change has been witnessed within the period before the virus outbreak and the present Covid-19 era. Taking into consideration a series of financial and economic indicators the degree of indebtedness existing within hospitality sector is of immense significance during a crisis situation. It is of prime significance for countries whose economic prospects are largely dependent on the revenue generated from hospitality sector. Therefore, the present research study has focussed into comparing the operational effectiveness of the UK hospitality sector for both before and present Covid-19 outbreak.
1.3 Research Aim
The aim of the research study is to determine the impact of Covid-19 on the financial and economic operational scope of the hospitality industry and further compare with business situation before the virus outbreak took place. The study has been conducted in the UK, that is largely known for a highly prosperous hospitality operational sector.
1.4 Research Objective
The objectives developed for this research study on the hospitality industry of the UK are as follows:
- To determine the financial and economic business scenario of the UK hospitality sector in the pre Covid-19 area.
- To determine the financial and economic business scenario of the UK hospitality sector due to the outbreak of Covid-19 area.
- To compare the financial and economic business scenario of the UK hospitality sector before and after the outbreak of Covid-19 virus.
1.5 Research Questions
The research question developed for this research study on the hospitality industry of the UK are as follows:
- What is the financial and economic business scenario of the UK hospitality sector in the Covid-19 era and how can it be compared with the pre-Covid-19 period?
1.6 Research Structure
The research study has been conducted in six parts, introduction, literature review, research methodology, data findings and analysis, discussion, conclusion and recommendations. Each of the six steps of the study has highlighted different aspects of the efforts exhibited in reaching a suitable conclusion to the research question. The introduction chapter unfurls the background study helped in framing research aim and objectives. Furthermore, literature review chapter has gathered information relevant to the research topic from secondary sources like news articles and journals relating to the topic. The research methodology chapter specified the type of methods used for collecting and analysing data, so that suitable answer to the research question is easily available. Furthermore, the data findings, analysis and discussion chapter provided the information collected exclusively for the research study followed by its detailed analysis. It also highlighted the degree of relevance and similarity that the literature review and data findings information hold as a means of gradually proceeding towards the stage of conclusion. Finally, the conclusion chapter provided a brief summary of the entire research study by highlighting the important points covered in the process.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
The literature review provided a detailed study of the existing secondary knowledge set relating to the economic and financial operational scenario of the hospitality industry. A comparative study has been done in this case relating to the present Covid-19 situation and before the global pandemic outbreak took place in the hospitality service sector. The literature review identified the notable factors that helps in defining the financial and economic environment of the hospitality sector and the degree of impact experienced due to the outbreak of Covid-19 virus. The consideration of multiple views in the literature review section has been considered as the basis for conducting the later stages of the research study.
2.2 Hospitality Sector
Hospitality sector is a crucial part of service industry associated with catering to the needs and demands of customers during their stay in a hotel or a dine-out in a restaurant (Research and Markets, 2020). The operational scope of the industry depends on the degree to which the organisation is able to address the satisfaction level of the customers by taking into consideration every minute aspect. The service operations are well distributed across a series of activities, starting right from lodging, travel arrangement and even amenities (Vokřínek, 2020). The hospitality operational activities are identified to help in the process of generating a large amount of revenue for local economies as the customers tends to spend a large amount of money in terms of availing the services. However, organisations operating in this sector required providing an array of services to make the customer experience and satisfaction level enjoyable and memorable.
2.3 Impact of Covid-19 on Financial and Economic Operational Environment
According to Campbell (2020), with more than two million active cases of people affected with Covid-19 across the world, governments went ahead with implementation of strict rule and regulations relating to social distancing. The decision was undertaken as a means of stop the further outbreak of the virus among people. The impact of the virus outbreak has been severely faced by all the operational industries, with the hospitality sectors being the most significant one. It is due to the governmental steps undertaken in reducing social contact among people taking place in hotels, restaurants and bars.
2.3.1 Financial Business Scenario
The outbreak of Covid-19 across the world has jeopardized the hospitality sector due to international travel ban and imposition of social distancing norms to prevent the spread of virus. As a result, the service industry experienced cancellation of corporate events, international seminars and meeting, sports and social events too (Deloitte, 2020). Furthermore, Covid-19 has resulted on job loss across the countries of Europe, Australia, China, the United States, each of them accounting for maximum number of visitors to the UK. With the loss in job of these nationalities, the countries are likely to slow down the demand for leisure and travel, causing impact on the UK tourism and hence its hospitality sector. It is to be also noted that total inflow of the tourists in the country is affected severely due to the sceptical point of views developed in the minds of people to travel overseas. The fear of getting infected is identified as one of the primary factors responsible for eroding the financial earning capacity of the hospitality sector largely.
The rapid spread of Covid-19 across the globe resulted in government as well as businesses to stress relevant importance on ensuring the safety of the people it tends to service. However, the safety considerations are identified to impose widespread operational implication and their corporate profit earning capacity. The financial business environment of hospitality industry is subjected to a sharp decline in its sales revenue which further impacted their sell-off in the global equity market (Deloitte, 2020). It is to be noted that the hospitality industrial sector is the first one to experience the operational turbulence and thereby focussing on undertaking suitable strategies to stay focus in their business aim. Furthermore, the Covid-19 situation resulted the hospitality industrial sector to quantify the degree of financial impact that the virus outbreak has on their business. The degree of impact on hospitality industry is immense, the revenue and supply chain to be strongly hit by it.
The decisions to temporary shut down hotels and restaurants as a means of implementing social distancing norms to prevent community outbreak of the virus resulted in developing a disruptive impact on the hospitality service operations (Dash, 2020). As a result, the organisations and investors are left with no other option than to mitigate the issues associated with working capital and cash followed by keeping close connection with the business stakeholders. Furthermore, the organisations operating in the hospitality sector are found to take extra effort for effective asset management due to the severe financial turmoil caused by Covid-19.Majority of the organisations are focussing on extending their cash flow forecasts for the upcoming six months (Deloitte, 2020). It is due to the uncertainty associated with how situations are likely to become in the future. The financial business management goal development process has assumed a realistic approach, with the consideration of notable base and downside scenarios. Such financial management business decision has been undertaken as a means of understanding the operational criticality developed due to Covid-19 outbreak on cash points and breaches relating to money lending covenants.
The hospitality service providers engaged themselves in managing their payment to the suppliers due to the emergence of financial uncertainty in the Covid-19 era. It also considered minimising all form of discretionary expenditures relating to both operational and capital management. The organisations have decided to reconsider and even postpone all form of capital and maintenance related expenditures. Such business decisions within hospitality sector emerged out of the necessity to conserve cash wherever possible and in every operational instance (Deloitte, 2020). The outbreak of Covid-19 also made the hospitality service providers to realise the relative importance of putting in an advanced revenue management for the purpose of responding in a quick and effective manner to market development processes. It also took into consideration of new pricing models as a means of dealing with operational consequences brought in by Covid-19 to hospitality industry. A large number of organisations experienced severe funding requirement forecasts due to the shutdown of operational services for implementing social distancing norms across the world. For the purpose of dealing with funding requirement, the organisations are left with no other option than to assess their equity and debt funding sources (Deloitte, 2020). Furthermore, the process involved consideration of new pricing models due to the decrease in spending tendency among people in hospitality services as a result of uncertainty that the outbreak of the virus has brought in with it.
The organisations realised the necessity of engaging in a transparent business relationship with the existing money lenders and make them actively engage in the process of mitigating the financial losses caused due to temporary operational shutdown. It is not possible for the industry and its operators to deal with the financial consequence single-handedly and hence the support and help of the money lenders has been identified to be of immense significance (Deloitte, 2020). Although, the organisations are open to the option of getting themselves engaged with new money lenders, who serve as a suitable solution to short-term funding issues, however, it seems to be very difficult in the long run. It is due to the high degree of interests and fees structure that will be levied on the hospitality service providers. The operational prosperity of the hospitality sectors has dropped so rapidly that the organisations are left with no other option than to rely on tax refund and financial relief measures as a means of dealing with their operational expenses.
2.3.2 Economic Business Scenario
The failure of negotiations in between the UK and European Union to reach the Free trade agreement, Brexit is considered to further multiply the operational challenges of the country’s hospitality industry. The profound impact of the virus outbreak is experienced primarily in the cities of Liverpool, London and Manchester since Europe and the US have been the major sufferers of the virus outbreak. However, the final impact of Covid-19 on the hospitality sector and its macro-operational factors is considered to vary in accordance to the duration of the pandemic and the restrictions imposed on travel and tourism. Furthermore, the response of the public is looked forward to further impact the degree of influence that Covid-19 will cause on the hospitality sector. The degree of economic impact is likely to become more prominent with the gradual lifting of the global travel restrictions. According to the prediction of GlobalData, the UK inbound tourist is likely to decrease by 35% in comparison to 2019 due to the massive impact of Covid-19 (Hospitality Net, 2020).
The hospitality sector operating in its maturity stage exhibited a collaborative effort as a means of satisfying its customers with high degree of quality service. However, the degree of economic impact of the pandemic was so severe that the organisations moved towards acceptance of new business opportunities. It comprised of undertaking new delivery ideas and promotion of staycation concept among customers (Deloitte, 2020). Furthermore, organisations in the hospitality sector were found to focus more on working towards developing standard operational procedures as a means of dealing with the negative impact of Covid-19 on their economic operations. The degree of economic crisis was so severe that the hospitality industry is in an urgent need for security plans that would help them in surviving the situation. Although the hospitality industry is experiencing a global slowdown with zero sales revenue, yet they have to bear enormous amount of fixed costs (V. Jain and P. Jain, 2020). The lockdown resulted in slowing down the degree of economic growth experienced due to full-fledged operations of hospitality service providers. The final outcome of this situation is identified to be highly catastrophic in nature, resulting due to economic slowdown. Furthermore, the entire world in on the verge of experiencing a severe recession in the hospitality sector in the future quarters due to the massive and cascading impact of the Covid-19 outbreak. The hotel booking experience monumental cancellations due to the travel restrictions and temporary shutdown of flights. The degree of cancellations has been so massive, that it resulted in developing a ripple impact on them.
The demand for hospitality services had dropped so much that it caused negative impact on GDP too and hence national income. As a result, the demand for high-end hospitality services is considered to decrease severely with the customers preference experiencing a rapid change. The economic uncertainty developed due to Covid-19 impacted the spending desire as well as capacity of employees largely. The degree of preference towards low-budget service providers is assumed to increase, which was initially perceived to be inferior by customers (Bianchi and Luciano, 2020). The fluctuations in customer demand is therefore identified as one of the severe economic impacts of Covid-19 virus outbreak on the hospitality industry.
The economic crisis developed by Covid-19 is comparable to the global financial crisis that took place in 2008 due to the substantial drop developed by it on the hospitality service demand among customers. The degree of economic severity is massive, since the virus outbreak has resulted in developing equal and considerable amount of impact on both hospitality service demand and supply too. On one instance, customers have reduced availing the hotel and restaurant service, while on the other hand, the social distancing norm imposed massive operational restrictions. The organisations are forced to reduce working hours, lower the number of employees and its operational capacity, thereby causing a negative impact on its degree of productivity (Deloitte, 2020). Each of these factors thereby questions the operational effectiveness of the service operations, and hence the reduction in their supply capabilities too. However, the operational sector has to bear the consequences of increase in marginal contracts and the supply contract too. The impact of Covid-19 on both supply and demand of hospitality sector at the same time is considered to result in high degree of unpredictability as a means of operational effectiveness (Campbell, 2020). To be precise, the future price level of organisations operating in this sector is highly questionable. The situation is well justified from the economic theoretical point of view, that states decrease in demand results in fall of price, however decrease is supply tends to cause increase in price. Therefore, it can be said that the hospitality industry is uncertain whether their operational price set in the Covid-19 or the post Covid-19 period will be steady or subjected to inflation or deflation.
2.4 Pre Covid-19 Operational Scenario
The hospitality industry is one of the notable operational sectors across the world due to the massive increase in customer spending capacity and the widespread investments made in terms of service delivery (Assaf and Josiassen, 2012). It is considered as one of the pioneers of socio-economic progress all across the world due to the creation of immense operational enterprises and employment opportunities. This along with export revenues and infrastructure development resulted in massive and continuous diversification of the hospitality service operations. It is referred to as one of the rapidly evolving economic business sectors across the globe (Chen and Lin, 2012).
2.4.1 Financial Business Environment
The financial performance of organisations operating in the hospitality sector is determined based on the degree to which it has successfully accomplished its economic business objectives (Chen, 2011). It experienced a cyclical financial growth rate due to favourable economic growth rate across the world and hence the customer to spend was hospitality services. According to De Grosbois(2012), depending on the favourable business environment, organisations was found to involve in frequent demand revival by getting engaged in customer service enhancement facilities. The customer service enhancement process was largely done based on the degree of financial sales revenue that an organisation successfully collected as a part of accomplishing their business objectives and catering to diversified hospitality needs of customers (Farčnik, Kuščer and Trobec, 2015).
The study conducted by Kim, Cho and Brymer(2013) highlighted that hospitality sector is subjected to high demand elasticity as more and more customers avail hospitality services across the world. The customer spending capacity favoured the financial business scenario largely with the consistent increase in the earning capacity of the working population. Furthermore, the emergence of middle-class section of the society in the developing nations of the world has too been identified as one of the notable factors impacting the financial favourability of the hospitality industry. On the other hand, Min et al. (2009) stated that high disposable income of the customers further impacted their discretionary spending level too. It served as a primary factor of influence for the hospitality industry to enjoy favourable financial prosperity. It is due to the rapid increase in travel and tourism activities of people followed any availing hospitality services. The increase in customer occupancy level served as a crucial tool for high financial results. Furthermore, Pereira‐Moliner, Claver‐Cortés and Molina‐Azorín, (2011) stated that high occupancy rate across the hospitality sector offers organisations to enjoy immense pricing power. The final outcome of such favourable financial business environment was found to allow them in enjoying high values of average room rent and revenue from each room available in hotels. Each of these two factors signified the healthy growth rate experienced by the industrial sector before the outbreak of Covid-19 largely.
2.4.2 Economic Business Environment
The macro-environmental factors like finance and economic critical in terms of analysing the growth and development prospects of the organisations operating in the concerned sector. The business operational scope of the hospitality industry is largely impacted by each of these two factors (Sainaghi, 2010). Chen (2010) stated that organisations operating in the hospitality sector experience different economic cycles. The economic performance and the relating conditioning factors things to serve as a key issue for future development. The organisations in this case is perceived as operating in a cyclical industry, impacted severely by the economic conditions of the state. The degree of operational sensitivity of hospitality service providers with the economic conditions is so severe that any form of economic crisis results in the organisations to experience severe uncertainty and turmoil (Assaf and Josiassen, 2012). It is due to the high degree of fixed costs that the hospitality service providers experience within their total operational cost. As a result, the high fixed costs tend to make the operational risks for the organisations highly severe. The business conditions play a very important role, especially during economic crisis situation or instances in which sales revenue contraction seems to be very high (Bodie, Kane and Marcus, 2013). Therefore, any form of fluctuation in sales revenue caused due to economic influences is detrimental to every organisation operating in this sector.
Tavitiyaman, Zhang and Qu(2012) stated that the growth in the hospitality industry has been reflected primarily due to presence of a large number of employment opportunities within the hospitality industry. The employment rate is found to experience an exponential growth rate with the emergence of diversified job opportunities like business managers, event organisers, contract caterers and even finance managers. With more and more customers looking forward to avail hospitality services, employment is found to be significant all across the globe. The hospitality industry is looked forward to deal with economic issues associated with unemployment and hence contributes largely to the development perspective of a country by alleviating it to some extent. Furthermore, the study conducted by Sainaghi(2010) stated that with increase in employment opportunities, the industry further helps in generation of revenue for local economies too. The customer spending on hotels and restaurants serves as a notable source of income for the country as well as the organisations too.
2.5 Research Gap
The literature review section has successfully collected information relating to the financial and economic business scenario of the hospitality industry in the pre and present Covid-19 scenario. In this regard, while taking into consideration several Jungle articles a significant gap has been identified in terms of specifying the operational context of the hospitality sector in the present Covid-19 scenario. Information relating to Covid-19 is only available in website articles. Furthermore, conduct journal articles on hospitality sector have not specified in great detail the UK business environment. Taking into consideration, this particular research gap, the student has proceeded further.
2.6 Summary
A wide range of differences has been observed within the economic and social business scenario of the hospitality sector due to the outbreak of Covid-19 and the period before its existence. The financial and economic prospect enjoy by the hospitality sector is largely at stake. It is due to the high degree of operational uncertainty relating to the standard protocol to be used for the purpose of getting back into the initial business prospect. The severity of the crisis situation is so massive, that the hospitality industry known for its financial and economic prospects is subjected to both demand and supply downfall. Moreover, the employment opportunities offered by the hospitality sector in the pre Covid-19 is in immense distress due to the restrictions imposed by governments all across the globe.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
3.1 Introduction
The pathway used for the purpose of a research study is known as methodology (Davies and Hughes, 2014). It helps in identifying a suitable pathway to be used for reaching the final results based on which the study will be concluded. It is of immense significance since the research methodology stage determines the effectiveness of the final results as a means of concluding the problem statement based on which the study has been conducted (Mackey and Gass, 2015). Primarily, accounts for the methods to be used for data collection and analysis. Therefore, research methodology helps a study to identify suitable methods to be deployed for data collection and analysis. It is integral to the process of ensuring each of the stages concerned with formulation and selection of a suitable research method to the final dissemination of the study results (Flick, 2015). It consists of several parts and sub-parts, which aids the process of identifying research methods taking into consideration the purpose and scope of the study. The following section highlights the research methodology considered for the study relating to analysis of the financial and economic business environment of the UK hospitality sector in the Covid-19 period and its comparison with before the virus outbreak situation.
3.2 Research Philosophy
The research philosophy governs the process associated with the development of knowledge set for the purpose of accomplishing a research topic. It is considered as the basis of a research study depending on which the further stages take place (MacDonald, 2012). With the selection of suitable research philosophy, information relating to the financial and economic business environment of the hospitality sector has been collected under the relative influence of Covid-19. There are four different types of research philosophies, realism, pragmatism, positivism and interpretivism (Kumar, 2019). Each of the research philosophies offers a different outlook as a means of defining a suitable framework for a research study. For this research study on Covid-19 and the UK hospitality sector, the interpretivism philosophy has been considered. This is because the research is going to use the secondary data set for arriving to a conclusion.
3.3 Research Approach
The research approach is used for the purpose of developing a conceptual plan, based on which a study goes with collecting data (Ledford and Gast, 2014). Data collection involves a series of stages, the research approach highlights how, when and where to proceed. It helps in narrowing down the process of data collection from a series of broad assumption. Therefore, the research approach in case of this study helped in identifying how to go ahead with data collection, interpretation and analysis. There are two types of research approach, inductive and deductive. Taking into consideration the present scope of study done in the context of the UK hospitality sector under the relative influence of Covid-19, the inductive research approach is used. The inductive research approach helped in considering deriving a new theory with social phenomenon.
3.4 Research Design
The research design helps in the process of developing a suitable framework, based on which a study takes place (Fletcher, 2017). The framework developed in the process acts as a suitable guide to be used for the purpose of making suitable choices relating to data collection and analysis. Upon considering a series of factors slide the scope and purpose of the research study, a suitable research design is selected. The present research study relating to the analysis of the financial and economic business environment of the UK hospitality sector in the Covid-19 period and its comparison with before the virus outbreak situation considers the use of exploratory research design. Exploratory research involves a severe investigation of the research question, considering numerable authentic data sources (Choy, 2014). Furthermore, it also helped in finding answers to a series of questions for the present research study, such as why and how the economic and financial environment experienced severe and operational turmoil due to the outbreak of Covid-19.
3.5 Research Method
The research method is the technique used for the purpose of discovering a new set of information for a specific research topic (S.K. Mangal and S. Mangal, 2013; J. Park an M. Park, 2016). There are two types of research methods, qualitative and quantitative, each having different tools for the purpose of collecting data. A combination of both the research methods is also used, referred to as mixed method (Brannen, 2017; Ragin, 2014). The research study relating to the analysis of the financial and economic business environment of the UK hospitality sector in the Covid-19 period and its comparison with before the virus outbreak situation considered the use of a quantitativemethod. The quantitative research method allows data collection which are numeric in nature and that could be collected from primary or secondary source (Sahu, 2013). The primary focus of the research method lies on understanding the numeric data collected from Bloomberg (Arghode, 2012). Since, the present research study request gaining detailed understanding of the financial and economic impact of Covid-19 on the hospitality sector of the UK and father compared it with situations before the pandemic occurred, subjective interpretation of data was found to be highly significant.
3.6 Data Collection
Data connection is defined as the process by which a research study collect data to be further measured according to certain variables identified for the purpose. It offers a systematic platform used as a means of a wide range of information based on which the research work which to be done (Bernard, 2017). There are two types of data collection process, primary and secondary, depending on the scope and purpose of the research study. Secondary data is significant in this case since financial and economic impact of Covid-19 on the hospitality sector compared to the initial days can only be gathered from the people involved in the business and hence affected due to it. As a result, the selection of, secondary data ensured the collected data to exhibit high degree of reliability and authenticity to be used for defining the present economic and financial business scenario of the UK hospitality sector. It is to be noted that out of the different methods of quantitative data collection, the secondary technique is also a reliable method (H.R. Bernard and H.R. Bernard, 2013). The secondary method of data collection provided a better, elaborated understanding of the research problem through the process of exploring the opinion, experience and behaviour of the respondents. Due to the Covid-19 outbreak, the interview has been conducted over phone for each of the respondents selected for this research study.
3.7 Sampling
Sampling is the process used in a primary data collection method as a means of identifying the total number of respondents from which data will be collected for the study. The sampling process helps in identifying the most suitable ones among a large population segment to have or impacted by the concerned problem scenario (O’Dwyer and Bernauer, 2013). For the present research study, simple random sampling has been used. It is due to the fact that the sampling technique ensures response collected from a single individual to have successfully reflected the point of view and perception on the entire population segment. There are 9 countries that has been selected from the sampling technique.
3.8 Data Analysis
The data collected for the research study was analysed used statistical analysis using Matlab. Statistical is used largely for the purpose of analysing quantitative data collected for a research study. (Jensen, 2013). (Clarke, Braun and Hayfield, 2015). A detailed analysis helped in the successful identification of the present economic and financial business scenario of the UK hospitality industry in the Covid-19 era. Furthermore, it also aided the process of comparing the results with the initial business environment of the industry before the outbreak of the virus situation.
3.10 Ethical Considerations
The research study has properly acknowledged each of the secondary data sources that has been used during literature review. Proper references for each of the information used has been provided to avoid any form of ethical issue.. The entire data collection process was accomplished by keeping in mind the principles associated with honesty and confidentiality. Furthermore, the data collected the research study was not used in any other purpose beyond this particular work.
3.11 Summary
The research methodology helped in identifying the quantitative method as the suitable one for this research study, taking into consideration the scope and purpose. The quantitative research method enabled the research study to consider a subjective interpretation of the problem scenario and thereby successfully reach a suitable stage of conclusion. The sample nations were selected using simple random sampling technique so as to make sure that the general overview of the entire population is obtained in the process. It also looked forward to ensuring that the conclusion has been derived by taking into consideration the point of view of the overall nations being associated with or impacted by the financial turmoil situation.
Chapter 4: Data Findings, Analysis and Discussion
4.1 Introduction
The data collected from the respondents using interview method has been elaborated in a detailed manner in the following section. Furthermore, themes have been identified from the data findings to go ahead with the process of data analysis using thematic technique. The data successfully collected from each of the 5 managers over telephone has been presented in an elaborated manner for the purpose of better understanding and analysis.
4.2 Data Findings
The data shared by each of the respondents for the questions asked to them during the interview process relating to the research topic is as follows:
Thematic Analysis
From analysis report, it is understood that most of respondents or employees of the hospitality industry agreed that the economic and financial structure of this sector has been drastically changed due to Covid-19 pandemic. The hospitality business is in a terrible state with sudden lockdown decisions of the government. As the government restricted people to stay safe distance from hotels and restaurants for effective social distancing, the operational scope of the industry is in severe distress. High degree of uncertainty involves relating to the standard operational procedures to be given by government as a means of resuming business.
Moreover, until and unless the travel ban across the globe is lifted up, it is very difficult to regain the same level of operational flow like before. The respondent also stated that the Covid-19 outbreak has resulted in the hospitality industry on the verge of surviving or experiencing a massive downfall. The amount of loss that the hospitality industry is experiencing can be easily quantified in the period of Covid-19. The strength of financial implication is so strong, that the revenue management process of even associated operations like supply chain also suffered the loss and operational uncertainty. The virus outbreak resulted in causing a disruptive impact of the financial sustainability that the industry and the organisations enjoyed before Covid-19. The hospitality service providers are left with no other option than to procure funds from shareholders as a means of ensuring their survival within the pandemic situation. The situation resulted in the organisations to restrict further investments and focus more on asset management. It is primarily due to lack of adequate information relating to future business operational scope of the industry.
The organisations are left with no other option than to extend their cash flow assets depending on the immense operational uncertainty forecasted in the future days to come. It also focussed on hospitality industry to manage payments to be made to suppliers for the purpose of dealing with the financial uncertainty that Covid-19 brought in the business operational activities. The organisations are left with no other option than to focus on cutting down all from of capital and operational aspects of finance, characterised as unwanted and extra in the period of crisis. The degree of operational scope and success, both remains critical, until and unless a proper solution to the virus outbreak comes in the market.
Figure Share Prices of Various companies
Various factors are there that has been changed due to Covid-19 situation within the hospitality industry such as revenue structure, effectiveness of operations and productivity. However, most of the respondents think that revenue structure of the hospitality industry has been changed mostly for this uncertain situation in all over the world. The customers are not willing to take travel and tourism services as they spend more money in the Covid-19 disease. Therefore, revenue structure of healthcare organization is increased and other organization under hospitality industry has been decreased. The hospitality sector experienced a cyclical financial growth rate. It is due to the high degree of favourable economic growth rate all across the world. In such a situation, customers were found to spend a large amount of money in the hospitality service sector. The business operational environment was so favourable that it allowed organisations to get engaged in enhancing the service prospect of hospitality sector as per customer demand.
Before the outbreak of Covid-19, the hospitality industry was subjected to high demand elasticity. It was primarily due to a large number of customers that the hospitality organisations catered too. Such operational effectiveness was primarily due to the increased customer spending capacity. A favourable income further enabled the customers to spend more, thereby allowing the organisations to enjoy high sales revenue growth.
The economic performance and the relating conditioning factors has played the role of enhancing the business scope of hospitality industry largely. As a result, the hospitality sector allowed every organisation operating within it to experience a cyclical growth rate. Such operational conditions thereby resulted in the industry to experience massive loss with the outbreak of Covid-19 virus.
Figure 1: Data Coding of Covid 19
Figure 3: Challenges faced by employees in hospitality industry
| U.K. | 634.1 | 4,970.3 | 190.2 | 2.5 | Began easing lockdown on June 8 | |
| Italy | 568.3 | 4,123.9 | 125.0 | 3.2 | Began easing lockdown on May 4 | |
| Brazil | 534.0 | 16,652.1 | 19.7 | N/A | No national lockdown | |
| U.S. | 528.4 | 16,922.6 | 226.6 | 2.8 | No national lockdown | |
| Germany | 115.4 | 2,895.6 | 127.0 | 8.0 | Began easing lockdown on April 20 | |
| Russia | 113.8 | 6,655.2 | 231.7 | 8.1 | Began easing lockdown on May 11 | |
| India | 41.8 | 2,215.6 | 24.9 | 0.5 | Began easing lockdown on June 8 | |
| Japan | 9.3 | 484.2 | 12.3 | 13.1 | State of emergency ended May 25 | |
| Mainland China | 3.3 | 61.1 | N/A | 4.3 | No nation |
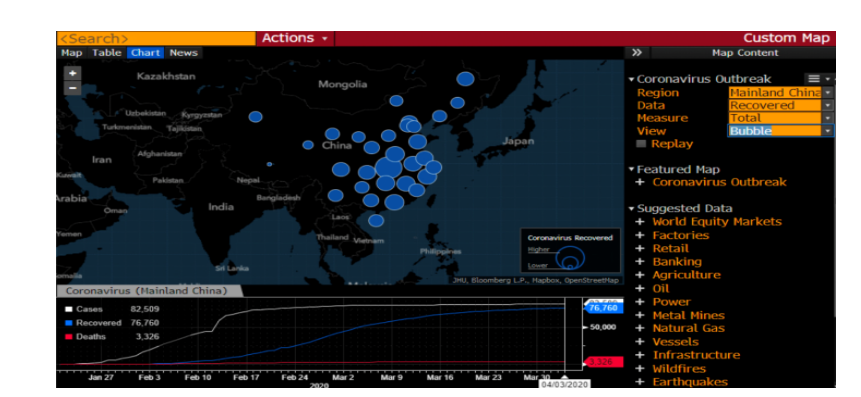
Due to this Covid-19 circumstances, the employees within the hospitality industry has faced different challenges such as they are terminated from organizations, not paid properly and lack of satisfaction is observed among them. 73.33% of total employees voted that unemployment rate is increased and employee retention rate is decreased as most of the organization provides their services through limited numbers of employees to maintain their revenue structure. The initial business situation was quite difficult.
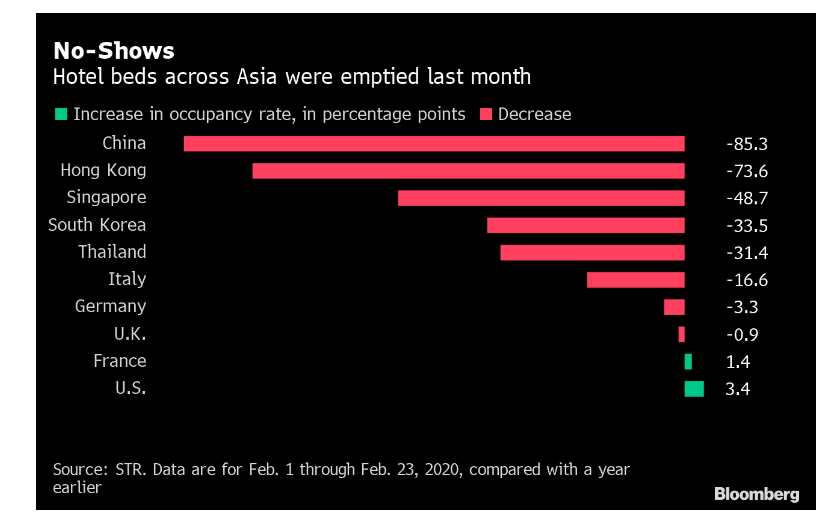
The sales revenue experienced massive positive growth rate with continuous increase in customer demand for hospitality services. Moreover, UK has been a notable destination of tourism for foreign customers, thereby contributing largely to the increased of hospitality service sales.
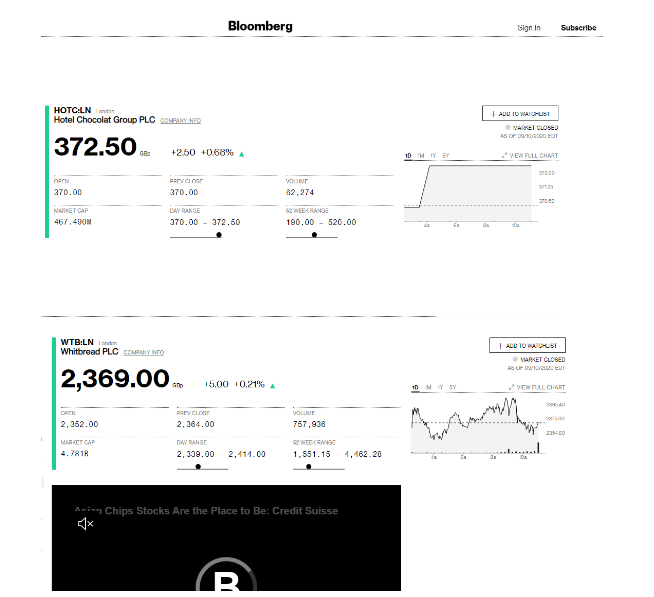
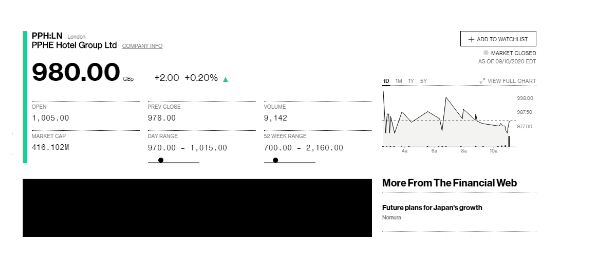
The flow of sales revenue before the outbreak of Covid-19 was spectacular in terms of enriching the economic prospects of the country. Taking into consideration, present business scenario in the present Covid-19 environment, it can be said that surrounding environment plays a critical role in terms of business prospects. The economic business environment of the hospitality industry has caused severe impacts on the hospitality service organisations operating in the major cities of UK. However, the degree of economic impact of Covid-19 can only be predicted and determined based on the total duration of the pandemic situation. Moreover, the travel restrictions and decrease in demand for hospitality services will result in a large number of people to lose their jobs. The hospitality organisations largely known for its widespread employment opportunities is at the verge of terminating a huge number of employees due to massive drop in service demand. In addition to that as the travel restrictions are uplifted, the economic severity can be further felt due to lack of adequate money for customers to spend on hospitality services. The decrease in the total number of customers is identified as the most striking economic impact of Covid-19 on the organisations operating in the hospitality sector. The economic impact is so severe that for organisations to survive the pandemic turmoil, a suitable solution lies in diversification of present business scope, by taking into consideration the new opportunities existing in the marketplace. Too effectively deal with the financial consequences associated with employment crunch, new business ideas like home delivery of food items maintaining all forms of social distancing norms have be adopted. The business diversification is mainly due to the necessity of helping organisations develop the ability to deal with the huge fixed cost associated with the hospitality service industry. Even in a period of zero sales revenue, the fixed costs continue to bother the service providers. The sudden drop in the sales revenue of hospitality industry can be described as developing a catastrophic impact on the entire economic environment of the country. It is due to the fact that economy of the UK is longer in a position to enrich from the hospitality service industry revenue. Moreover, the cancellations in customer bookings further contributed to the development of a ripple effect on the economy of the country largely. If such situation consists for a prolonged time period, the hospitality industry is likely to feel the worse recession even in the future days to come.
The economic and financial business environment determines the ability of an organisation to experience high success rate. Till date before the outbreak of the virus, the hospitality industry of the UK was in a booming state. Customers from across the world contributed to the sales prospect of the organisations largely, across different aspects and operational scope of the hospitality service industry. The degree of success was so massive, that hospitality sector occupied the top position in terms of infrastructure development and service innovation for customers.
4.3 Data Analysis
The data findings from each of the respondents from interview method has been analysed by taking into consideration some themes. Each of the themes have been identified based on the responses shared by the managers on the present research topic. Furthermore, the identified themes identified from interview responses have also been analysed in accordance to the information collected during literature review as a means of effective data analysis and discussion for the research study on Covid-19 and its impact on hospitality industry.
Cash Flow: The degree of financial impact was so severe that organisations are required to extend their cash flow assets. The cash flow management is largely dependent on the degree of operational uncertainty that the industry has forecasted to experience in the future. The financial business scenario of the hospitality industry is in severe distress and hence considering stakeholder helps largely for managing effective flow of cash required for surviving the great loss caused due to Covid-19. The organisations have cut down all form of expenses that involved in the process of increasing the service operational scope for the customers.
Demand and Supply Fluctuation:The outbreak of Covid-19 created a simultaneous drop in demand and supply for the organisations engaged in hospitality services. The drop in service demand has been primarily identified due to the restrictions imposed by the government and necessity of social distancing among people. Furthermore, the fear developed within the minds of the customers to getting infected upon visiting a restaurant or a hotel is also found as one of the primary factors impacting the economic business environment.
Job opportunities: The hospitality industry is largely known for its employment opportunities. It has been identified as one of the primary aspects of the UK hospitality sector before the virus came and affected each of the organisations and the people associated with it. The lack of service demand and social distancing norm not only resulted in the organisations to close down but also had to terminate employees as a means of bearing their operational expenses. In such a situation, a large number of people lost their prospective jobs and the hospitality industry is in a position of considering ways for its survival in this period of crisis situation.
4.4 Discussion
The information shared by the respondents is largely supported by the information collected from the study conducted by Deloitte (2020) which highlighted how Covid-19 has jeopardized the hospitality sector of the UK largely. According to the study, financial business environment of hospitality industry is subjected to a sharp decline in its sales revenue which further impacted their sell-off in the global equity market. The degree of financial loss experienced in the process is easily quantified since Covid-19 resulted in shutdown of business activities followed by imposing a series of travel restrictions (Dash, 2020). As a result, the hospitality industry in on the verge of experiencing immense loss. Furthermore, the Covid-19 outbreak has resulted in the organisations and investors are left with no other option than to mitigate the issues associated with working capital and cash followed by keeping close connection with the business stakeholders. It thereby made the industry realise the relative importance of effective management of financial asset for the future days to come. From a comparative point of view, the pre Covid-19 period witnessed massive cash flow profitability with a large amount of money being spend on discretionary expenses. However, the virus outbreak has completely altered the operational context of the hospitality industry largely. The operational prospect of the business in the future is unknown. In such a situation, the organisations are left with no other option than to extend their operational cash flow forecast for the coming quarters. The financial management scope of the industry is relying upon worst case scenarios and hence left with no other option then ensure smooth flow of cash from the business stakeholders. The financial crisis caused by Covid-19 has resulted in developing severe cash point and money breaches from the covenants who have invested heavily in the once prosperous business sector. The outbreak of Covid-19 and the pandemic situation is a catastrophic event for the hospitality business. The degree of severity in this case is massive since people are living in a fear of community outbreak of the virus. As a result, even after the government lifts the lockdown, it is uncertain whether the business will come back in its original operational effectiveness or not. The operational fragmentation of the hospitality sector of UK is subjected to severe risk with a large number of organisations calling of their business with permanent shutdown of hospitality services.
The hospitality sector seems to be jeopardized. The international travel ban and imposition of social distancing norms have made our lives, people associated with hospitality industry to experience immense misery. We have experienced a massive cancellation of bookings made by customers, which has not been witnessed in the last 8 years of the respondent’s professional experience with the hospitality industry of the UK. The country known for offering some of the well-known hospitality destinations to people across the globe is left with no idea relating to how to resume business and the future business strategies.
The primary concern for hospitality sector of the UK lies in the fact that that major consumer markets are on the verge of an impending hob loss. Each of the countries, witnessing maximum customers of the hospitality industry are experiencing a severe economic crisis. In such a situation, the hospitality industry known for its leisure services will not be considered as suitable option even if the travel ban and operational restrictions uplifted by the government. The entire operational system got disarranged in a manner that seems to be nearly impossible in regaining to initial days of prosperity.
The fear of getting infected will restrict people from socialising. Hence, restaurants and pubs, identified as suitable destinations for socialising will be left empty, with no customer. In addition to this, the foreign customers of the hospitality industry too suffer from wide range of sceptical views relating to getting infected upon visiting an international country and further avail its hospitality services. A large amount of time will be required even after things come in normal for the hospitality organisation to enjoy the same level of profit.
The profit seems to be in negative with the sales revenue being nil. The sharp decline in the sales earning capacity further impacted the operational sell-off the organisation operating in the hospitality sector across the equity market of the world. The financial turbulence caused due to Covid-19 resulted in hitting the hospitality industry largely and that too in the first instance even before the number of infected persons started increasing. From then till now, the organisations operating in this sector is coming across massive loss of revenue. In such a situation, it is relatively difficult for the organisations to remain focussed in their strategic business objectives.
The financial crunch is so severe that the hospitality service providers are left with no other option than to focus in terms of managing supplier payment. A wide range of financial costs relating to discretionary expenses that organisations undergo as a part of business operation is in deep trouble. The hospitality service industry known for its business innovation and creativity has postponed all its future customer service enhancement initiatives due to the severe financial crunch that the outbreak of Covid-19 virus has brought in with it. In such a situation, the organisations are heavily relying on advance revenue management to be used as a means of effectively dealing with future service market development process.
The outbreak of Covid-19 resulted in developing a simultaneous drop in demand and supply of the hospitality services. The drop in service demand is due to the travel restrictions imposed by the government and necessity of social distancing among people. It also accounted for fear developed within the minds of the customers to getting infected upon visiting a restaurant or a hotel. The shift in customer preference from availing hospitality services can be largely witnessed. On the other hand, the social distancing norms further resulted in organisations to alter their overall operational process. A series of operational restrictions relating to total number of employees, operational hours and time to time sanitisation impacted the supply capability of the organisations largely. In such a situation, the organisations are found to experience severe operational downfall due to lack of productivity. The simultaneous impact of both demand and supply side of the hospitality business operations is identified as the most significant economic impact developed due to the pandemic situation occurred as a result of Covid-19 outbreak.
The economic business environment of hospitality sector of the UK is in such a situation, that it is difficult to predict and develop a suitable price level that would help the organisations in regaining their operations. The pricing strategy and level to be used in the future when business starts operation is uncertain since both the demand for the service and supply capability of the organisations have been impacted in this context of Covid-19. The organisations have no information relating whether the future economic outlook of the business demands the consideration of steady price rate or is likely to experience deflation. Furthermore, the occurrence of an inflation too cannot be ignored taking into consideration the present economic business scenario.
A series of operational restrictions relating to total number of employees, operational hours and time to time sanitisation impacted the supply capability of the organisations largely (Campbell, 2020). In such a situation, the organisations are found to experience severe operational downfall due to lack of productivity. The impact of Covid-19 on both supply and demand of hospitality sector at the same time is considered to result in high degree of unpredictability as a means of operational effectiveness. The organisations are uncertain about the future price level to be used as a means of effectively accomplishing their business operations. According to the report published by Deloitte (2020), the simultaneous impact of both demand and supply side of the hospitality business operations is identified as the most significant economic impact developed due to the pandemic situation occurred as a result of Covid-19 outbreak. From a comparative point of view, it is quite evident that the hospitality sector that enjoyed predominant sales demand is largely at stake amidst the global pandemic situation. The demand and supply effectiveness of the organisations identified in the pre-virus outbreak period is identified to suffer the most in the present Covid-19 period.
4.5 Summary
The data findings section has highlighted the point of views of the respondents collected during the interview process. Furthermore, taking into consideration detailed responses, suitable themes have been developed as a means of analysing the data according to the research question and objectives developed for the study. The thematic analysis done in this context, further enabled the process of discussion, wherein the responses of the managers and the information collected during the literature review process has been used. From each of these sections, it has been identified, that initially the hospitality industry of the UK enjoyed high degree of operational prominence as well as success. However, since the business environment got severely influenced due to Covid-19, the situations changed drastically.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Future Implications
5.1 Summary
Based on the data findings, it can be said that the hospitality sector of the UK needs to exhibit a positive attitude and stay focus on the degree of severity that Covid-19 has exhibited on their financial aspect of doing business. The shift in customer preference from availing hospitality services can be largely witnessed. On the other hand, the social distancing norms further resulted in organisations to alter their overall operational process. However, it is to be noted that before Covid-19, the favourable operational scenarios, financial and economic resulted in the hospitality business sector of the UK to experience widespread economic and financial prospects. There were a large number of organisations operating in the sector, catering to the different needs and demands of the customers. Furthermore, it is to be noted that the organisations also enjoyed high sales revenue followed by contributing largely to the economic conditions of the country largely in terms of sales revenue and employment. The favourable operations in the period before Covid-19 was and the rapid decline in operational effectiveness of hospitality industry during Covid-19 was due to the increased influence of macroeconomic business environment factors. The growth and development prospect of each of the organisations associated with hospitality industry is largely governed by the degree to which the surrounding environment is favourable for the customer to avail the services offered.
The hospitality industry of the UK witnessed a 97% decline in its ability to earn sales. It has been primarily identified due to a large number of factors. To be precise, a series of operational restrictions relating to total number of employees, operational hours and time to time sanitisation impacted the supply capability of the organisations largely. In such a situation, the organisations are found to experience severe operational downfall due to lack of productivity. The simultaneous impact of both demand and supply side of the hospitality business operations is identified as the most significant economic impact developed due to the pandemic situation occurred as a result of Covid-19 outbreak. As a result, the hospitality organisations experienced a massive shift in customer preference from availing hospitality services. Furthermore, it is to be noted that the lockdown and travel restrictions imposed by the government all across the world resulted in altering the operational process and further cutdown of employment opportunities within the sector. A significant change has been witnessed within the period before the virus outbreak and the present Covid-19 era.
A large number of organisations experienced severe funding requirement forecasts due to the shutdown of operational services for implementing social distancing norms across the world. For the purpose of dealing with funding requirement, the organisations are left with no other option than to assess their equity and debt funding sources. The necessity of funds for the organisations have been primarily identified due to the imposition of operational restrictions relating to total number of employees, operational hours and time to time sanitisation impacted the supply capability of the organisations largely. Therefore, organisations lacked adequate capability required for ensuring the operational productivity.In such a situation, it is very difficult for the UK based hospitality sector to revive to its initial flow of operation. The organisations can revive in full form if some miracle happens that takes away the virus from the globe or a vaccination is done to prevent people from getting infected.
5.2 Future Implications
The future of the hospitality industry is uncertain until Covid-19 disappears from the society completely. Otherwise, it is not possible to uplift the financial and economic busines environment of the organisations. The fear of the virus outbreak along with necessity of maintaining social distancing norms is one of the primary factors hindering the growth prospect of the industry. Until and unless a vaccine is invented, people will continue to live in fear and refrain themselves from socialisation and hence hotels and restaurants. The future operational context of the industry seems to be gloomy with high degree of uncertainty relating to regaining back its operational prospect before the outbreak of Covid-19.
Reference List
Arghode, V., 2012. Qualitative and Quantitative Research: Paradigmatic Differences. Global Education Journal, 2012(4).
Assaf, A.G. and Josiassen, A., 2012. Identifying and ranking the determinants of tourism performance: A global investigation. Journal of Travel Research, 51(4), pp.388-399.
Assaf, A.G. and Josiassen, A., 2012. Identifying and ranking the determinants of tourism performance: A global investigation. Journal of Travel Research, 51(4), pp.388-399.
BBC, 2020. Coronavirus: Hospitality industry ‘faces thousands of closures’. [online] Available at: <https://www.bbc.com/news/business-51923804> [Accessed 9 July 2020].
Bernard, H.R. and Bernard, H.R., 2013. Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Sage.
Bernard, H.R., 2017. Research methods in anthropology: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Rowman & Littlefield.
Bianchi, G., and Luciano, L., 2020. Economic Theories On COVID-19’s Impact On Hospitality And Tourism. [online] Available at: <https://www.hospitalitynet.org/opinion/4099628.html> [Accessed 9 July 2020].
Bodie, Z., Kane, A. and Marcus, A.J., 2013. Essentials of investments (pp. 532-537). Taipei: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Brannen, J. ed., 2017. Mixing methods: Qualitative and quantitative research. Routledge.
Campbell, A., 2020. COVID-19: Impact of coronavirus on the hotel and leisure market. [online] Available at: <https://www.fieldfisher.com/en/insights/covid-19-impact-of-coronavirus-on-the-hotel-and-le>[Accessed 9 July 2020].
Campbell, A., 2020. COVID-19: Impact of coronavirus on the hotel and leisure market. [online] Available at: <https://www.fieldfisher.com/en/insights/covid-19-impact-of-coronavirus-on-the-hotel-and-le> [Accessed 14 July 2020].
Chen, C.M. and Lin, Y.C., 2012. Does better service induce higher profitability? Evidence from Taiwanese Hospitality Industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(4), pp.1330-1332.
Chen, M.H., 2010. The economy, tourism growth and corporate performance in the Taiwanese hotel industry. Tourism Management, 31(5), pp.665-675.
Chen, M.H., 2011. The response of hotel performance to international tourism development and crisis events. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 30(1), pp.200-212.
Choy, L.T., 2014. The strengths and weaknesses of research methodology: Comparison and complimentary between qualitative and quantitative approaches. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 19(4), pp.99-104.
Clarke, V., Braun, V. and Hayfield, N., 2015. Thematic analysis. Qualitative psychology: A practical guide to research methods, pp.222-248.
Dash, J. 2020. Covid-19 impact: Travel, hospitality stare at revenue loss of Rs 5 trillion. [online] Available at: <https://www.business-standard.com/article/economy-policy/covid-19-impact-travel-hospitality-stare-at-revenue-loss-of-rs-5-trillion-120041800801_1.html> [Accessed 14 June 2020].
Davies, M.B. and Hughes, N., 2014. Doing a successful research project: Using qualitative or quantitative methods. Macmillan International Higher Education.
De Grosbois, D., 2012. Corporate social responsibility reporting by the global hotel industry: Commitment, initiatives and performance. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(3), pp.896-905.
Deloitte, 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on the hospitality industry. [online] Available at: <https://www2.deloitte.com/nl/nl/pages/consumer/articles/impact-of-covid-19-on-the-hospitality-industry.html> [Accessed 9 July 2020].
Farčnik, D., Kuščer, K. and Trobec, D., 2015. Indebtedness of the tourism sector in Mediterranean countries. Tourism economics, 21(1), pp.141-157.
Fletcher, A.J., 2017. Applying critical realism in qualitative research: methodology meets method. International journal of social research methodology, 20(2), pp.181-194.
Flick, U., 2015. Introducing research methodology: A beginner’s guide to doing a research project. Sage.
Global Data, 2020. COVID-19 Outbreak Has Jeopardized UK Hospitality Sector. [online] Available at: <https://www.hotelnewsresource.com/article110449.html> [Accessed 14 June 2020].
Hospitality Net, 2020. COVID-19 Outbreak Has Jeopardized UK Hospitality Sector, Says GlobalData. [online] Available at: <https://www.hospitalitynet.org/news/4098446.html> [Accessed 9 July 2020].
Jain, V. and Jain, P., 2020. Impact of Covid-19 on Independent/Budget Hotel Industry in India. .[online] Available at:<http://bwhotelier.businessworld.in/article/Impact-of-Covid-19-on-Independent-Budget-Hotel-Industry-in-India/25-04-2020-190282/> [Accessed 9 July 2020].
Jensen, K.B. ed., 2013. A handbook of media and communication research: Qualitative and quantitative methodologies. routledge.
Jones, P., Hillier, D. and Comfort, D., 2016. Sustainability in the hospitality industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
Kim, W.G., Cho, M. and Brymer, R.A., 2013. Determinants affecting comprehensive property-level hotel performance: The moderating role of hotel type. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 34, pp.404-412.
Kumar, R., 2019. Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. Sage Publications Limited.
Ledford, J.R. and Gast, D.L. eds., 2014. Single case research methodology: Applications in special education and behavioral sciences. Routledge.
MacDonald, C., 2012. Understanding participatory action research: A qualitative research methodology option. The Canadian Journal of Action Research, 13(2), pp.34-50.
Mackey, A. and Gass, S.M., 2015. Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Mangal, S.K. and Mangal, S., 2013. Research methodology in behavioural sciences. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
Min, H., Min, H., Joo, S.J. and Kim, J., 2009. Evaluating the financial performances of Korean luxury hotels using data envelopment analysis. The Service Industries Journal, 29(6), pp.835-845.
Mok, C., Sparks, B. and Kadampully, J., 2013. Service quality management in hospitality, tourism, and leisure. Routledge.
O’Dwyer, L.M. and Bernauer, J.A., 2013. Quantitative research for the qualitative researcher. SAGE publications.
Park, J. and Park, M., 2016. Qualitative versus quantitative research methods: Discovery or justification?. Journal of Marketing Thought, 3(1), pp.1-8.
Pereira‐Moliner, J., Claver‐Cortés, E. and Molina‐Azorín, J.F., 2011. Explaining the Strategic Groups–Firm Performance Relationship: A Multilevel Approach Applied to Small and Medium‐Sized Hotel Companies in Spain. Journal of Small Business Management, 49(3), pp.411-437.
Ragin, C.C., 2014. The comparative method: Moving beyond qualitative and quantitative strategies. Univ of California Press.
Research and Markets, 2020. COVID-19’s Impact on Hospitality, 2020 Market Report. [online] Available at: <https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/covid-19s-impact-on-hospitality-2020-market-report-301042147.html> [Accessed 14 June 2020].
Sahu, P.K., 2013. Research methodology: A guide for researchers in agricultural science, social science and other related fields (p. 432). Nadia: Springer.
Sainaghi, R., 2010. A meta‐analysis of hotel performance. Continental or worldwide style?. Tourism Review.
Tavitiyaman, P., Zhang, H.Q. and Qu, H., 2012. The effect of competitive strategies and organizational structure on hotel performance. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
Vokřínek, B., 2020. Covid-19 Impacts on European Hospitality. [online] Available at: <https://www.cushmanwakefield.com/en/united-kingdom/insights/covid-19-impacts-european-hospitality> [Accessed 14 June 2020].
Werner, S.V., Zhao, G., Friebe, K. and Kelly, A., 2020. Cross-border: COVID-19 and the Hospitality Sector – The big questions facing UK hoteliers and lessons we can learn from China. [online] Available at: <https://www.twobirds.com/en/news/articles/2020/global/covid-19-and-the-hospitality-sector-the-big-questions-facing-uk-hoteliers-and-lessons-we-can-learn> [Accessed 14 July 2020].






