Financial Risks From High Leverage
Financial Risks From High Leverage: The Analysis Of Chinese Real Estate Industry
Table of Contents
1.6 Outline of research methodology. 6
Chapter 2: Literature Review.. 8
2.1 Real estate (RE) business structure. 8
2.2 Financing sources of real estate. 9
2.2.1 Real estate funding from foreign and domestic sources. 9
2.2.2 Debt and leverage in Real Estate industry. 10
2.3 Economy of real estate: demand and supply. 11
2.4 Purchasing power of customers. 11
2.5 Financial risks faced by Chinese RE industry. 12
2.6 Link between debt and leverage with the financial risks associated with the RE sector 14
2.7 Impact of Financial risk on performance of the real estate industry in China. 15
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Research background
The real estate market of China is called one of the most important sectors in the World’s economy. This sector plays an irreplaceable role in consumption and investments by contributing a huge amount to the global GDP (Liu, Wang and Yang, 2017). Annual housing activity in this country, based on both construction and other property related goods and services, accounts for more than 29% of the GDP of China (theguardian.com, 2021). This amount is more than 10% to 20% of the most developed countries. It has been reported that in 2017, the sales revenue of Chinese real estate industry has become 83,841.784 RMB which was 66,632.482 RMB for 2016 (ceicdata.com, 2022). It indicates a continuous growth in the real estate sales revenue in China.
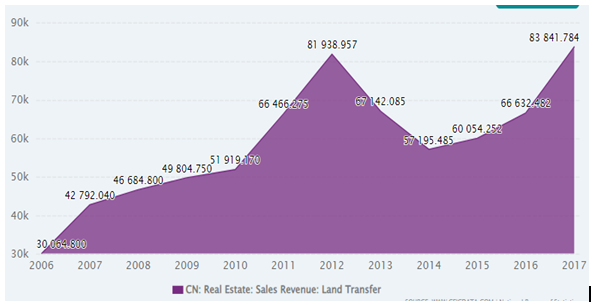
Figure 1.1: Sales revenue of real estate in China (2006-2017)
(Source: ceicdata.com, 2022)
However, high leverage or high debt ratio has become one of the most concerning financial risks for the real estate industry in China. For instance, it has been reported that the second-largest real estate developer in China, Evergrande has rattled the world with its huge debt amount of $300 billion (forbes.com, 2021). Similarly, some other real estate developers in this country, such as Kaisa have reported diminishing cash flow due to missing payments.
The second issue is about the rising housing prices which causes several financial risks in this industry. It has been reported that housing prices in this country have increased by 99% in the past few decades and it overleveraged debt among the real estate developers as the rate of selling decreased accordingly (forbes.com, 2021). Similarly, it has been highlighted by Liu, Wang and Yang (2017) that the high housing price in China has become far beyond the scope that the people in this country can bear.
On the other hand, it has been reported that in the present time, real estate developers are struggling to get financing as it has created a negative sentiment among the investors with the high leverage issues of Evergrande (cnbc.com, 2021). This kind of tight financial condition has created a relatively challenging environment for property developers or real estate companies in China. Apart from that current report has shown that troubles in the Chinese real estate industry can negatively affect the global economy including the United States (US) and due to this reason, it has been warned by the US central bank that on-going property woes of China could elevate “financial stresses (business-standard.com, 2021). High debt issue of China’s most indebted developer, Evergrande, is one of the key reasons behind high leverage or other financial risks associated with this sector.
Apart from that as per the report of Consumer News and Business Channel (CNBC), the property market of China could experience more pain even if Evergrande’s crisis would be mitigated (cnbc.com, 2021). According to this report, this particular crisis indicates more pain in the future. For instance, in the last several days in November 2021, apart from Evergrande, other real estate developers have reported liquidity problems. In addition to that, in Hong Kong, the Chinese property stocks trading have mostly fallen during this period and Evergrandelost about 1.3% of its debt (cnbc.com, 2021).
1.2 Research problem
As per the above discussion, the first issue faced by the Chinese real estate sector is the high-debt ratio or leverage which is mainly highlighted by Evergrande. The second issue is raising housing processes for which the rate of property sales is decreasing causing the further issue of high-debt ratio of the real estate developers. The third problem is about the development of negative sentiment regarding the financial performance of the real estate companies to the investors which has caused a challenging environment. The force issue is the downfall of the financial performance of the Chinese real estate industry that causes the global economy. Moreover, the liquidity issue is also a key concern in this industry. This peer study has focused on these specific issues to recommend effective ways of managing such financial risks and improve financial performance in the future.
1.3 Research Aim
The aim of this research is to examine the financial risks from high leverage debts in the real estate industry in China.
1.4 Research objectives
The key objectives of this research are-
- To find out the financial risks faced by the Chinese real estate industry
- To evaluate the impact of high leverage, debts/transactionsto induce financial risk in the Chinese real estate sector
- To analyze the impact of financial risks on the performance of the real estate industry in China [NNH1]
1.5 Research questions
- What financial risks are faced by the real estate companies in China?
- How do high leverages debts/transactionsimpact on the level of financial risks in the Chinese real estate industry?
- How do financial risks influence performance of the real estate sector in China?
- What are the effective ways of mitigating the identified risks for improving performance of the Chinese real estate industry?
Hypotheses
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): High debt or leverage has significant impact on the financial performance of real estate companies.
Null Hypothesis (H0): High debt or leverage has no significant impact on the financial performance of real estate companies.
1.6 Outline of research methodology
In this report, a secondary qualitative method would be followed to collect and analyze data. In this particular context, different relevant financial data such as Debt equity, debt-to-asset, interest coverage ratio (independent variables) and Net profitability or revenue (dependent variable) of last four years would be collected. These financial data would be collected from annual reports of three renowned real estate companies in China namely Evergrande, Kaisa and Sino Group. Based on this collected data different statistical analyses such as correlation, regression, descriptive, Anova analyses would be performed to meet the specific research aim.
1.7 Dissertation structure
The entire research paper would be represented in six different chapters including introduction, literature review, methodology, Results and Analysis, Discussion and Conclusion. In this first chapter, based on the specific problems the aim, objectives and questions have been designed and the rest of the research would be organized as follows. In the next chapter, different views of different authors regarding financial risk of the Chinese real estate industry are discussed by reviewing a number of existing literatures. Different relevant theories, concepts of leverages and debts, and the current scenario of the Chinese real estate industry would be documented in this chapter. In this chapter, the used methodologies would be covered including data collection and analysis methods, research philosophy, approach, design and so on. The collected data would be analysed in Chapter 4 to obtain research findings. Chapter five would contain the detailed discussion of the research findings to relate back to the literature review, this chapter, it would be possible to know whether the specific research questions are properly answered or not. However, in the last or conclusion chapter, the key findings of this research would be concluded along with the mention of limitations, improvement and future scopes. This chapter would help to understand whether the research objectives are met.
Chapter 2: Literature Review[NNH2]
In this chapter, different views of different authors regarding the financialrisk and leverage of the Real Estate industry of China are reviewed. The findings from this chapter would help to find out the literature gap based on which the method of conducting this present study can be demonstrated.
2.1 Real estate (RE) business structure
According to Liu and Xiong (2020), the RE market is not only a crucial part in the economy of China but also an integral component of its financial system. RE is one of the largest industries in China and there will be more than 103,262 real estate developers in China in 2020. This statistic also shows that the number of RE developers in this country is increasing day by day. From this context, it has been understood that the RE industry is one of the key contributors to the national economy of this country. Apart from that the Return of Investment (ROE) of this sector has become 14.268% in 2019 from 14.254% and 13.85% in 2018 and 2017 respectively (ceicdata.com, 2022). It indicates that, up to 2019, this industry has risen its profit generation without needing as much capital.
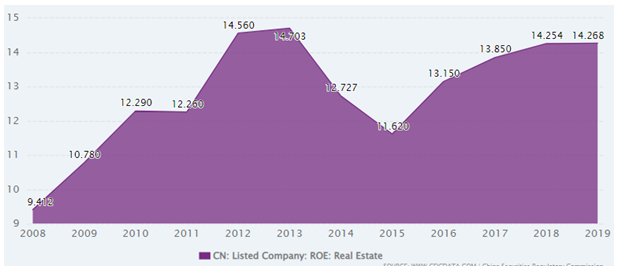
Figure 2.1: Return of Investment (ROE) of RE companies in China (2008-2019)
(Source: ceicdata.com, 2022)
According to Zhang et al. (2018), the overall business process and growth of the RE industry depends on the commercial banks of both their own and foreign countries. The business structure of this industry in China is different from the other countries. For instance, there is no specific private ownership of land in this country and for this reason; rights of using the land can only be obtained based on the land lease system. In this particular system, up to 70 years of land lease is granted for residential purposes (globalpropertyguide.com, 2021). It has also been reported that Mainland Chinese residential and commercial property investment has increased by 3% to 8% in 2017 (globalpropertyguide.com, 2021). On the other hand, it has been revealed by (Chen and Li, 2017), the RE industry plays a crucial role in China’s economic development. This study has also highlighted the report released by the National Bureau of statistics; this industry has contributed 6.5% GDP in 2016. It has also been revealed by Liu and Xiong (2020) that in 2017, total sales of China’s RE industry has become 13.37 trillion RMB which is 16.4% of China’s GDP. These results indicate that the financial contribution of the RE industry of China to its GDP is increasing per year. Supporting this statement, it has been highlighted by Wang (2021) that the RE sector has become one of the key drivers of the economic growth engine of China. Thus, all the existing relevant literatures support that the healthy development of this industry directly influences the development of the national economy of China.
2.2 Financing sources of real estate
The real estate companies are funded from a range of sources for effectively operating their business activities which are discussed below.
2.2.1 Real estate funding from foreign and domestic sources
According to Gholipour, Tajaddini and Pham (2020), there is a key relationship between default on mortgages (DOM) and real estate market transparency (RET). Hence, mortgage based loans are an effective source of financing for this industry. On the other hand, it has been revealed by Allen et al. (2019), shadow banking is an innovation in this country that enriches the financing channels of the economy of China. This innovation in the funding system has increased the likelihood of affiliated loans for the investment or growth of the RE industry. This research has also shown that the construction and RE industry has received 12.2% of the total affiliated loan amounts by considering this industry important for China’s economic development. From this point of view it has been understood that the bank loan is one of the most important funding processes in the real estate industry in China. In this similar manner, it has been stated by Gaudêncio, Mazany and Schwarz (2019) that a huge amount of loan is granted from different national and international banks to develop business in the real estate industry. Thus, this literature also indicates that bank loans are one of the key domestic sources of financing in China’s real-estate industry.
On the contrary, it has been revealed by Cao and Zong (2019) that since 2000, the amount of foreign direct investment (FDI) in China’s RE industry has been increasing every year. As per this study, the market of RE in China accounted for 20% of the total FDI in China in 2006. This amount has become 34.62 billion us dollars of the total FDI in 2014 and 19.66 billion us dollars in 2016. Thus, the findings of this study indicates that FDI is one of the most important sources of funding for the RE industry in China. Similarly, it has been pointed out by Hanemann and Huotari (2018) that the European FDI to real estate industry in China was EUR 10 billion per year up to 2015 and this amount has become EUR 8 billion in 2016-2017. Findings of this study also indicate that FDI is a great financing source for this industry. On the contrary, this study has also highlighted that due to increased informal investment restrictions, the amount of FDI inflow to the Chinese RE industry from Europe has decreased since 2016 (Hanemann and Huotari, 2018). However, reviewing these relevant literatures, it has been understood that both domestic and FDI are the sources of funding for the RE industry in China.
2.2.2 Debt and leverage in Real Estate industry
As discussed above, loans from different commercial national and international banks are the main sources of funding of the RE companies. It has been stated by Barclay, Heitzman and Smith (2017), that using a significant amount of leverage is a great and effective way to increase the RE portfolio as well as overall profit. In the RE industry, the investors use leverages to buy properties which cost more than the amount of money available to them. However, based on the contracts, the leverages are needed to be painted on time. Oppositely, many RE developers become unable to pay back the due averages on time and this aspect is responsible for the high debt or leverage related financial risks associated with this industry (Febriyanto et al., 2018). Similarly, in China, the RE sector is facing several financial risks due to high leverage or debt. As for this particular reason, proper maintenance of debt and leverage is important to avoid a number of financial risk I the RE sector.
2.3 Economy of real estate: demand and supply
Demand and Supply is one of the most widely used theories in the business management process in the RE industry. As per the Demand and supply theory, when there is a high demand of different residential or commercial properties in the market, there is a lack of quality property supply (Glaeser et al., 2017). In this particular context, the price of the properties is also increased. On the contrary, at the time of low demand, the supply of quality properties becomes increased and it sometimes causes reduction in the property prices. On the other hand, it has been revealed by Su and Qian (2020) that increased demands for properties increases the rate of investment of the property developers. Taking it into account, it has been argued by Glaeser et al. (2017) that as this high demand and investment increases overall property prices, it further causes decline in demand as many people cannot afford the high prices of the properties. In this way, the demand and supply theory is directly related to the investment and performance of the RE industry in China and other countries.
2.4 Purchasing power of customers
As per the study of Zhang et al. (2018), Green housing has become one of the most trending purchasing intentions among the young customers in China. Focusing on this particular aspect, the government of this country encourages the real estate developers to develop green buildings based on the “Green Building Action Initiatives” taken by the Chinese General Office of the State Council in 2013. Similarly, it has been stated by Ullah, Sepasgozar and Wangn (2018) that ‘go greenery’ or green housing is one of the key demands among the young customers and it has a direct link with the technological innovation. On the contrary, it has been argued by Chen, Hui and Wang (2011) that 46% of the Chinese homebuyers and 30% of residential consumers regret their decisions regarding the technologically undeveloped companies. Oppositely, it has been revealed by Liu, Wang and Yang (2017) that due to high housing prices, many people in China are unable to afford such properties and it in turn has become a key financial risk of this industry in terms of debt and leverages. On the other hand, it has been found by Yan (2019) that as a result of the prudent monetary policy implementation, domestic housing prices in China have shown an obvious rising trend during 2012-2016. As for this particular reason, the ability of the home buyers has been reduced and it indicates a significant decline in their purchasing power and overall market demand. From this context, it has been understood that increased housing prices are responsible for the decline in purchasing power of the consumers in the RE industry in China.
2.5 Financial risks faced by Chinese RE industry
There are a range of issues faced by the RE industry across the world and in the present time, this industry in China is facing a financial crisis that has become a barrier in its further development. For instance, Cao and Zong (2019) has highlighted that in 2008, the financial crisis from the US housing market has negatively impacted the FDI inflow in the Chinese RE industry. This price bubble has created an uncertain macroeconomic environment in China that further affected both the supply and demand of housing. Supporting these aspects, it has been stated by Kaaresvirta, Kerola and Nuutilainen (2021) that due to debt issues associated with Evergrande, one of the largest RE developer, other companies in this industry are facing an issue related to leverage, debt and investment. As a result, their share prices in the past few years have fallen significantly. Hence, availability of sufficient funding sources and high debt or leverage are the concerning financial risks associated with this industry.
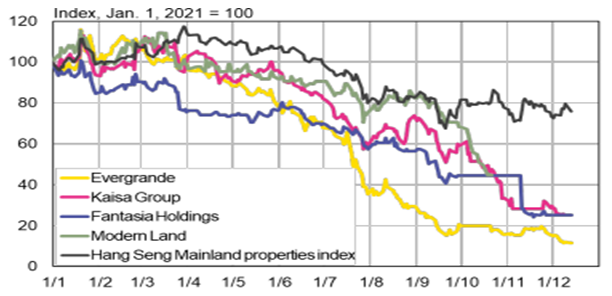
Figure 2.2: Share price Hong Kong-listed RE companies
(Source: Kaaresvirta, Kerola and Nuutilainen, 2021)
According to Li and Ponticelli (2020), many large property developers in China, such as Evergrande, is in the brink of bankruptcy as it is above $300 billion in debt and has 1.6 million undelivered apartments. Similarly, it has been reported that this RE developer has to pay interest on above $1.2bn of international loans in December 2021 but it has missed the deadline (bbc.com, 2021). Hence, bankruptcy is one of the key financial risks associated with this industry. On the other hand, it has been pointed out by Cao and Zong (2019), that due to raised debt and leverages, the RE industry in China has become insolvent and illiquid because this interest amount is 50% more than its liability. These literatures have shown that bankruptcy and insolvency are the concerning financial issues in this industry.
As discussed above, the restrictions in the FDI are increased and as a result, the amount of FDI inflow is decreasing (Hanemann and Huotari, 2018). Similarly, reviewing the literature of Cao, J. and Zong (2019), it has been found that in 2016, the the total amount of FDI into the real estate industry was 19.66 billion us dollars while it was 34.62 billion us dollars in 2014. Hence, reduction in the rate of FDI in the RE sector is also a concerning financial risk in China.
Reviewing the above-mentioned literature, it has been understood that FDI rate reduction is a financial risk in the country. On the other hand, it has also been found that FDI is one of the key funding sources for the RE industry in the UK (Hanemann and Huotari, 2018). Due to this reason, the RE sector in this country is facing an issue related to unavailability of funds to complete their planned tasks. Apart from that it has been observed that because of the debt or high leverage issue related to the largest property developers in China, a negative sentiment has been created regarding the performance of this industry (cnbc.com, 2021). Supporting this aspect, it has been stated by Zhang et al. (2018) that, due to the high debt or high leverage issue, a negative scenario has been created in the RE sector of the country and due to this reason, the property developers are facing issues in getting loans.
2.6 Link between debt and leverage with the financial risks associated with the RE sector
Financial risks of an organisation or industry refer to the inability to manage its financial leverage and debts. On the other hand, it has been stated by Chen and Li (2017), that the asset financed by the can serve as collateral for the debt; it further lowers the default risk for the lender. Contradicting this statement, it has been stated by Wang (2021) that the inability of the organisations to pay debts on time creates a financial risk. In contrast, it has been revealed by Brown (2000) that highly leveraged owner-managed properties liquidated assets during the commercial real estate decline of the late 1980s. It has also created buying opportunities for the people in the country. According to Aalbers (2019), the housing or real estate industry in China is facing a concerning issue related to higher debt. On the other hand, it has been found by Gokmenoglu and Kaakeh (2020) that liquidity, tangibility, and non-debt tax shield (NTDS) have significant impact on the capital leverage of the RE companies in China. However, in the past few decades, the RE industry of China is facing high leverage issues which in turn impacts their overall financial performance. As per the report of 2021, due to increased debt ratio, it has become an issue for the Chinese property companies to get loans and invest in its development (cnbc.com, 2021). As a result, the overall development of this industry is faced with a barrier.
2.7 Impact of Financial risk on performance of the real estate industry in China
As per the findings of Xie (2016) the key financial risks faced by the real estate industry in China include increased interest rate risk, raised exchange rate risks, credit risk, liquidity risk and policy risk. According to this study finding, due to the increased rate of bank loan interest in China, the property developers face an issue to pay the due debts on time. In turn results in the high leverage or liquidity issue in the overall business process of this industry. On the other hand, because of the increased exchange rate, a significant money flow has taken place in the real estate market of China. As a result, real estate prices in China have increased which further has created a price bubble. This price bubble is responsible for the uncertainty in this industry and this uncertainty has negatively influenced the ability and decision of investment in the RE development.
Supporting these aspects, it has been highlighted by Allen et al. (2019), that capital of the RE developers in China and many other countries come from mainly commercial banks as loans that in turn creates liquidity risks to these banks. This statement is supported by Xie (2016) and it has been revealed that in most of the cases, the commercial bank becomes unable to withdraw the money in a short time and it results in money shortage followed by liquidity issues. In this similar context, the RE developers cannot get enough loans further and this unavailability of funding directly and negatively impacts the performance as well as growth of these companies. It has been reported that the debt issue faced by the Chinese RE industry is likely to cause a period of stagnation that affects both the global and domestic economy (cnbc.com, 2021). Reviewing these literatures, it has been found that different financial risks decline the performance of the RE industry in China in the past few years.
2.8 Literature Gap
Reviewing a number of relevant literatures, it has been known that any financial issues are faced by the RE sector in China and as a result overall performance of this sector has declined. In a similar manner, it has also been seen that high leverage or debt issues are one of the key concerns in this industry. It has also been found from the literature review that this high leverage issue negatively impacts the financial performance of this industry. However, the existing literature is not able to provide any insight about the effective ways of managing such identified financial risks associated with the RE industry in China. Apart from that, there is a limited amount of relevant literature which has been conducted focusing on the financial risks and leverage issues in the Chinese RE industry. Focusing on these gaps, this current study is going to find out the effective ways of risk management for the development of this industry.
References
Aalbers, M.B., (2019) Financial geography II: Financial geographies of housing and real estate. Progress in Human Geography, 43(2), pp.376-387.
Allen, F., Qian, Y., Tu, G. and Yu, F., (2019) Entrusted loans: A close look at China’s shadow banking system. Journal of Financial Economics, 133(1), pp.18-41.
Barclay, M.J., Heitzman, S.M. and Smith, C.W., (2017) Leverage and taxes: evidence from the real estate industry. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 29(4), pp.86-95.
bbc.com (2021) Evergrande: China property giant misses debt deadline, available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-58579833 [Accessed on: 27th December 2021]
Brown, D.T., (2000) Liquidity and liquidation: evidence from real estate investment trusts. The Journal of Finance, 55(1), pp.469-485.
business-standard.com (2021) China’s real estate problems could hurt global markets, warns US Fed, Available from: https://www.business-standard.com/article/international/china-s-real-estate-problems-could-hurt-global-markets-warns-us-fed-121110901730_1.html [Accessed on: 24th December 2021]
Cao, J. and Zong, Y., (2019) Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in China’s Real Estate Market. Guangdong, 1, pp.1432-06.
Chen, J., Hui, E.C. and Wang, Z., (2011). Perceived risk, anticipated regret and post-purchase experience in the real estate market: The case of China. Housing Studies, 26(03), pp.385-402.
Chen, Q. and Li, F., (2017) Empirical analysis on efficiency of listed real estate companies in China by DEA. Ibusiness, 9(03), p.49.
cnbc.com (2021) China’s property market could see more pain, even as Evergrande crisis seems to be abating, Available from: https://www.cnbc.com/2021/11/09/china-property-market-may-see-more-pain-though-evergrande-crisis-may-ease.html [Accessed on: 24th December 2021]
cnbc.com (2021) China’s property market debt could weigh on the country for years, economist George Magnus warns, Available from: https://www.cnbc.com [Accessed on: 26th December 2021]
cnbc.com (2021) Developers struggle to get financing, Available from: https://www.cnbc.com/2021/11/26/chinas-real-estate-uncertainties-persist-fueling-market-anxiety.html [Accessed on: 27th December 2021]
Febriyanto, F.C., (2018) The effect of leverage, sales growth and liquidity to the firm value of real estate and property sector in Indonesia stock exchange. EAJ (Economic and Accounting Journal), 1(3), pp.198-205.
forbes.com (2021) What Can We Learn From The Real Estate Developer Crisis In China?, Available from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2021/12/06/what-can-we-learn-from-the-real-estate-developer-crisis-in-china/ [Accessed on: 27th December 2021]
Gaudêncio, J., Mazany, A. and Schwarz, C., (2019) The Impact of Lending Standards on Default Rates of Residential Real-Estate Loans. ECB Occasional Paper, (220).
Gholipour, H.F., Tajaddini, R. and Pham, T.N.T., (2020) Real estate market transparency and default on mortgages. Research in International Business and Finance, 53, p.101202.
Glaeser, E., Huang, W., Ma, Y. and Shleifer, A., (2017). A real estate boom with Chinese characteristics. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 31(1), pp.93-116.
globalpropertyguide.com (2021) Chinese property investment overseas sets new records, despite restrictions, Available from: https://www.globalpropertyguide.com/news-chinese-property-investment-overseas-sets-new-records-despite-restrictions-3578 [Accessed on: 26th December 2021]
globalpropertyguide.com (2021) How difficult is the property purchase process in China?, Available from: https://www.globalpropertyguide.com/Asia/China/Buying-Guide [Accessed on: 26th December 2021]
Gokmenoglu, K. and Kaakeh, M., (2020) Investigating the determinants of capital leverage: the case of China’s real estate sector. International Journal of Economics and Business Research, 20(3), pp.288-309.
Hanemann, T. and Huotari, M., (2018) EU-China FDI: Working towards reciprocity in investment relations. MERICS Papers on China, 3.
Johnston Ross, E. and Shibut, L., (2015) What Drives Loss Given Default? Evidence from Commercial Real Estate Loans at Failed Banks. FDIC Center for Financial Research Paper, (2015-03).
Kaaresvirta, J., Kerola, E. and Nuutilainen, R., 2021. China’s real estate sector and the impacts of its possible disorder on Chinese economy and the euro area.
Li, B. and Ponticelli, J., (2020). Going bankrupt in China (No. w27501). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Liu, C. and Xiong, W., (2020) 7. China’s Real Estate Market (pp. 183-207). Princeton University Press.
Liu, Y., Wang, S. and Yang, M. (2017), July. Financial Risk Analysis and Prevention of Chinese Real Estate Enterprises. In 2017 3rd International Conference on Economics, Social Science, Arts, Education and Management Engineering (ESSAEME 2017). Atlantis Press.
Luo, S. and Murphy, A., (2020) Understanding the exposure at default risk of commercial real estate construction and land development loans.
Patel, K. and Vlamis, P. (2006) An empirical estimation of default risk of the UK real estate companies. The Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics, 32(1), pp.21-40.
statista.com (2021) Annual growth rate of foreign direct investment (FDI) in the real estate industry in China from 2008 to 2016, Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/917490/china-fdi-growth-rate-in-real-estate-industry/ [Accessed on: 26th December 2021]
Su, X. and Qian, Z., (2020) State Intervention in Land Supply and Its Impact on Real Estate Investment in China: Evidence from Prefecture-Level Cities. Sustainability, 12(3), p.1019.
theguardian.com (2021) End to China’s estate market boom could spell trouble, Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/oct/15/chinas-booming-real-estate-market-could-spell-trouble-for-the-economy#:~:text=China’s%20real%20estate%20market%20has,sector%20in%20the%20world%20economy.&text=Taking%20into%20account%20construction%20and,typical%20of%20most%20developed%20nations. [Accessed on: 26th December 2021]
Ullah, F., Sepasgozar, S.M. and Wang, C., (2018) A systematic review of smart real estate technology: Drivers of, and barriers to, the use of digital disruptive technologies and online platforms. Sustainability, 10(9), p.3142.
Vlamis, P., (2007) Default risk of the UK real estate companies: is there a macro-economy effect?. The Journal of Economic Asymmetries, 4(2), pp.99-117.
Wang, B. (2021) The Evolving Real Estate Market Structure in China. In Understanding China’s Real Estate Markets (pp. 9-19). Springer, Cham.
Xie, W., (2016) May. The Analysis of Financial Risks of Real Estate in China. In Conference Paper: 2nd International Symposium on Social Science.
Yan, N., (2019) Study on the influence of monetary policy on real estate price in China. Journal of Service Science and Management, 12(02), p.152.
Zhang, D., Cai, J., Liu, J. and Kutan, A.M., (2018) Real estate investments and financial stability: evidence from regional commercial banks in China. The European Journal of Finance, 24(16), pp.1388-1408.
Zhang, D., Cai, J., Liu, J. and Kutan, A.M., 2018. Real estate investments and financial stability: evidence from regional commercial banks in China. The European Journal of Finance, 24(16), pp.1388-1408.
Zhang, L., Chen, L., Wu, Z., Zhang, S. and Song, H., (2018) Investigating young consumers’ purchasing intention of green housing in China. Sustainability, 10(4), p.1044.
ceicdata.com (2022) View China’s China Real Estate: Sales Revenue: Land Transfer from 1988 to 2017, Available at: https://www.ceicdata.com/en/china/real-estate-enterprise-all/cn-real-estate-sales-revenue-land-transfer [Accessed on: 10th January 2022]
ceicdata.com (2022) China Listed Company: ROE: Real Estate, Available at: https://www.ceicdata.com/en/china/financial-data-of-listed-company-return-on-equity-roe/cn-listed-company-roe-real-estate[Accessed on: 10th January 2022]
Cao, J. and Zong, Y., 2019. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in China’s Real Estate Market. Guangdong, 1, pp.1432-06.
[NNH1]I deleted the fourth because it’s not a research objective. If any, that would be your recommendation in the end
[NNH2]An introductory paragraph would help here to show the outline of your LR.
Overall, the literature is okay. You just need to provide a connecting sentence between one section/sub-section to another, so it won’t been seen as disparate sections.



