An Analysis Of Impact Of Marketing Strategies On Growth Of Tourism
An Analysis Of Impact Of Marketing Strategies On Growth Of Tourism: A Comparative Study Of India & China
Table of Contents
2.1 Effect of marketing strategies on the growth of tourism sector 5
2.2 Comparison of the growth of tourism sectors between India and China. 6
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
Travel and tourism are one the largest industries across the world as it contributes a significant amount to the world Gross domestic product (GDP). For instance,as per the report of the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), the contributions of Chinese and Indian tourism sectors to their national GDP in 2019 were the same, USD 9,170 billion (wttc.org, 2022). On the contrary, in 2020, this sector of India and China contributes 4.7% and -59.9% to the world GDP (statista.com, 2022).
On the other hand, total revenue of the Chinese tourism sector has started to decrease since 2018 accounting 12.3% to -61.1% in 2020 (statista.com, 2022). It has been reported that the Covid-19 pandemic crisis is the key reason behind this significant fall in the overall revenue of the tourism sector in China. On the contrary, as its revenue was also decreasing during 2018 and 2019, it indicates an issue in the strategies or overall business management process of this industry. On the other hand, the Indian tourism industry has generated $247.3 billion in 2018 (business-standard.com, 2022).
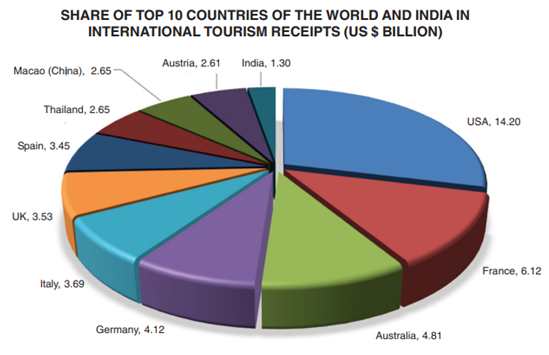
Figure 1: Market share of different countries in tourism receipt (2021)
(Source: tourism.gov.in, 2022)
The above figure shows that in 2021, the share of China and India to international tourist receipts is US$2.65 billion and US$1.30 billion respectively and it indicates better growth of the Chinese tourism sector compared to India (tourism.gov.in, 2022). Previous studies have revealed that marketing strategies play an important role in this growth as these strategies help to attract customers by increasing awareness (Hole and Snehal, 2019). As for this reason, it is important to find out the strategies followed by these two countries and impact on these strategies on this sector’s growth.
1.2 Research Problem
It has been seen that due to Covid-19 pandemic situation, the revenue as well as the total contribution of both India and China’s tourism sectors to the GDP has significantly decreased (statista.com, 2022). On the other hand, in 2020, China has experienced a greater decrease in GDP contribution than India. In contrast, the reports show that, before the pandemic crisis, the growth of the Chinese tourism sector was greater compared toIndian tourism sector (investindia.gov.in, 2022 and tourism.gov.in, 2022). Hence, it is an issue for both the countries to improve this situation. This proposed study can shed light on this issue by identifying and recommending effective marketing strategies for further growth.
1.3 Research Aim
The aim of this proposed comparative study is to analyse the impact of marketing strategies on the growth of the tourism sector in the context of China and India.
1.4 Research Objective
The key objectives of this researcher are-
- To analyse the impact of marketing strategies on the tourism sectors growth
- To evaluate the comparison of tourism sectors’ growth between India and China
- To find out the marketing strategies followed by Indian and Chinese tourism sectors for the purpose of growth
1.5 Research Questions
The research questions are as follows.
- How do marketing strategies influence growth of the tourism sector?
- What are the differences of marketing strategies between China and India and their impact on the tourism business sectors?
- What are the effective marketing strategies of the Chinese and Indian tourism sectors?
2. Literature Review
2.1 Effect of marketing strategies on the growth of tourism sector
According to Wang and Wong (2020), tourism marketing is a collective name for different types of marketing strategies applied by businesses in the tourism sector. This covers hotels and different other types of accommodations with airlines, services regarding car rentals, venues for entertainment, travel agents and different other kinds of accommodations. However, Entinaet al., (2021) have argued that the main purpose of marketing is to develop business, making it unmatchable to the rivals, drawing customers and improving brand awareness. There are several modern marketing strategies of tourism, which make effective usage of the internet, with different adverts, websites, platforms used in social media and emails. This helps in ensuring considerable growth of the sector. Rasul, Zaman and Hoque (2020) have added that one of the most important marketing strategies for tourism is capitalisation voice search. With the development of the technology for voice recognition, marketers have the opportunity of exploring different avenues. For instance, hotels are now applying smart hubs for providing voice search abilities in the rooms. This provides an important tourist information source. Liu, Pan and Zheng (2019) are of the opinion; application of artificial intelligence is another important marketing trend. It helps travel websites to analyze the booking made in the past for creating personalized offers for all the people. On the other hand, Wang and Wong (2020) have stated that chat bots are not that useful for guaranteeing quick customer response time. Entinaet al., (2021) have pointed out the personalized marketing strategy, which mainly targets people with the help of pertinent messages for marketing. This is responsible for appealing to them on an individual level.
2.2 Comparison of the growth of tourism sectors between India and China
From the research of Wang and Wong (2020), it can be stated that the tourism industry in India is currently growing exponentially. In the year 2018, it accounted for 6.4 trillion rupees or 6.6% of the GDP of the nation. The travel and tourism council is known for supporting more than 39.5 million of jobs, which is responsible for 7.7% of the country’s employment. The projected growth of the industry on an average is 7.9% from the year 2013 to the year 2023. However, Liu, Pan and Zheng (2019) have argued that Chinese tourism is expanding more than the tourism in India. China is regarded as the world’s third most visited nation. Nearabout 55.98 million tourists from across the world visited the country in the year 2019 resulting in 45.8 billion inflow of foreign exchange income. China is projected to become the biggest tourist nation of the world and one of the largest for all kinds of overseas travels.
2.3 Difference between the marketing strategies of India and China for growing the tourism industry at National as well as International Level
According to Khartishviliet al., (2019), in tourism sector the nations need to play a vital part to promote marketing in national as well as international level. According to Sharma (2017), in order to promote marketing, the strategies for understanding the consumer needs and application of digital facilities are essential. In India, the marketing strategy is being formulated considering the 7Ps of Marketing Mix. For promoting the Indian Tourism at international-level a proper effort on advertising of the essential trades, fair and festivals have been initiated. Apart from that Global Print Campaign has been done for highlighting Indian Tourism Products on international platform. Initiatives such as “Bharat Parv” and “World Tourism Day” are effective international marketing strategy impacting the growth of tourism sector (Sharma, 2017). In national level, “Atithi Devo Bhaba” advertise campaigns has brought a significant growth within the sector. Moreover, digital initiatives related to green tourism are the strategies along with influencer marketing are being incorporated for attracting tourist arrival in various areas (Sharma, 2017).
On the other hand, Nguyenand Yang(2021) have opined that in China national level of marketing strategy incorporates brand tourism and regional cooperation for enhancing the marketing growth. For international level strategy China has incorporated four initiatives “515 Strategy”, “Tourism Plus”, “Regional tourism strategy” and “Belt and Road strategy”. With the “515 Strategy” has been developed aiming at maintaining the quality of the tourism products with five goals-10 actions-52 specific initiatives. “Tourism Plus” strategy has described the development of old-age tourism, modern-tourism, health-tourism, business-tourism and research-tourism; whereas; “Regional tourism strategy” which aims as sustainable development of the rural areas of China. “Belt and Road” strategy is a way to the development of the connectivity for the tourist arrival within the nation (Nguyen and Yang, 2021).
3. Research Methodology
3.0 Research onion
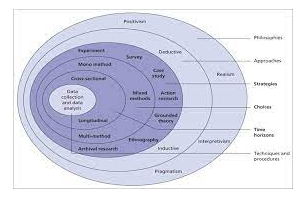
Figure 2: Research Onion
(Source: Melnikovas. 2018)
3.1 Research Philosophy
Research philosophy stands for the belief through which the data regarding a particular phenomenon needs to be gathered, analyzed and used to get a fruitful outcome. The implementation of proper research philosophy helps the research to gain sufficient, new and reliable knowledge regarding the selected research objects. Research philosophy is the basis of the research that involves the selection of research strategy problem formulation, data collection and analysis (Cazeaux. 2017). There are mainly four types of research philosophy that can be used in research to get the appropriate result, this includes, positivist, realist, pragmatism and interpretivism. This research, therefore, has selected the positivist research philosophy. The positivist research philosophy adheres the factual knowledge through proper observation method, that includes proper measurements.
3.2 Research Approach
A research approach is something that reflects the plans and procedures of different species based on broad assumptions related to data collection, analysis and interpretation. There are mainly three types of research approaches that can be used to address the research problems. These include, deductive, inductive, and abductive (Alase, 2017). This research has adopted the deductive research approach. The deductive research approach refers to the process that is associated with the scientific investigation. In this way it helps to develop a hypothesis based on the existing theories to test the link between the gathered knowledge and realities.
3.3 Research Choice
The selection of research methods helps in identifying and utilizing the strategies, processes, and techniques to collect appropriate data and evidence regarding the selected topic. There are mainly two choices of research methods, that includes, quantitative and qualitative research methods. The quantitative research mainly focuses on collecting and analyzing the numerical data collected through practical experiences (Rodriguez, and Smith, 2018). On the other hand, the qualitative method involves non-numerical data collection and analyzing processes to have a clear understanding of concepts, experiences and opinions. This research has adopted a mixed research method that includes both primary and secondary data collection and analysis regarding the marketing strategy and growth of tourism between India and China.
3.4 Research Strategy
Research strategy refers to the process of developing a step-by-step plan that guides the thoughts and efforts of the researcher by enabling them to conduct the research in a systematic manner.There are different types of research strategy that includes case study, quantitative surveys, qualitative interviews and action-oriented research. This research has selected the quantitative survey through which the research will collect related data from direct respondents. In this case, the candidates will be from the tourism industry and they will belong from different positions from booth India and China (Moser, and Korstjens, 2018). Along with that, it will also conduct a qualitative research strategy through which it will collect data from the written research papers by different researchers.
3.5 Data Collection Method
The mixed data collection method that researchers have adopted for the current paper is certainly an important aspect for gathering and analyzing significant amounts of data. The next data collection method has two different forms, which includes primary the collection method and the secondary data collection method. The primary data collection method incorporates interviews and questionnaires where the researcher needs to present face to face or with the Internet in front of the respondents (Alase, 2017). Moreover, in the secondary data collection method the research will gather using different scopes of secondary sources. That includes books, already researched papers, articles, magazines, and newspapers. The selection of mixed methods will therefore help the researcher in gathering both the primary and secondary sources of information more firmly and appropriately.
3.6 Data Analysis
The mixed data analytics Technique has been selected by the researcher to analyze all kinds of data collected through mixed methods (Moser, and Korstjens, 2018). This method will therefore help the researcher in understanding the prospects and frameworks of data using a variety of different Frameworks. Such strategies ultimately ensure positive alignment with the research objectives and findings of research questions in a much accurate and efficient manner
3.7 Research Ethics
It is important to follow the research ethics in an appropriate manner to avoid any type of legal intervention in a research paper (Brown, Spiro, and Quinton, 2020). This research is also following the research ethics for the same reason. This includes:-
Plagiarism: This research was completely free from plagiarism issues. Ity ensures to include the work done by the researcher only and also based on own understanding.
Copyright: The required data that has been gathered from other researchers has also been cited properly to avoid any type of copyright issue.
Consent: As it contains a primary survey method thus it ensures that all respondents will receive a consent form prior to participating in the survey. Their identity and other information will be kept confidential and only after getting their consent will they participate in the survey.
3.8 Gantt Chart
| Activities | 1st to 2nd week | 3rd to 4th weeks | 5th to 6th weeks | 7th to 8th week | 9th to 10th week | 11th week |
| Topic selection | ||||||
| Research structure | ||||||
| Literature review | ||||||
| Primary/ and Secondary data collection | ||||||
| Data analysis | ||||||
| Conclusion and recommendation | ||||||
| Submission of the research study |
(Source: Self-created)
References
Alase, A., 2017. The interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA): A guide to a good qualitative research approach. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 5(2), pp.9-19.
Brown, C., Spiro, J. and Quinton, S., 2020. The role of research ethics committees: Friend or foe in educational research? An exploratory study. British Educational Research Journal, 46(4), pp.747-769.
business-standard.com, 2022. Tourism Sector Records Growth Of 6.7% In 2018, Available at:https://www.business-standard.com/article/news-cm/tourism-sector-records-growth-of-6-7-in-2018-119043000665_1.html#:~:text=The%20domestic%20tourism%20sector%20generated,%3A%20Unlocking%20the%20Opportunities’%20noted.&text=By%202029%2C%20the%20sector%20is,million%20people%2C%20directly%20and%20indirectly. [Accessed on: 15/01/2021]
Cazeaux, C., 2017. Art, research, philosophy (p. 202). Taylor & Francis.
Entina, T., Karabulatova, I., Kormishova, A., Ekaterinovskaya, M. and Troyanskaya, M., 2021. Tourism Industry Management in the Global Transformation: Meeting the Needs of Generation Z. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 23(2), p.130.
Hole, Y. and Snehal, P., 2019. Challenges and solutions to the development of the tourism and hospitality industry in India. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 8(3), pp.1-11.
investindia.gov.in (2022) The Tourism and Hospitality industry is one of the largest service industries in India, Available at: https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/tourism-hospitality [Accessed on: 15/01/2021]
Khartishvili, L., Muhar, A., Dax, T. and Khelashvili, I., 2019. Rural tourism in Georgia in transition: Challenges for regional sustainability. Sustainability, 11(2), p.410.
Liu, J., Pan, H. and Zheng, S., 2019. Tourism development, environment and policies: differences between domestic and international tourists. Sustainability, 11(5), p.1390.
Melnikovas, A., 2018. Towards an explicit research methodology: Adapting research onion model for futures studies. Journal of Futures Studies, 23(2), pp.29-44.
Moser, A. and Korstjens, I., 2018. Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. European journal of general practice, 24(1), pp.9-18.
Nguyen, N. and Yang, R., 2021. A comparative study: China’s and Vietnam’s inbound tourism marketing strategies. Available at: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/501550/Nguyen_Nguyen%20and%20Yang_Rui.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y [Accessed on: 15/01/2022]
Rasul, T., Zaman, U. and Hoque, M.R., 2020. Examining the pulse of the tourism industry in the Asia-Pacific region: a systematic review of social media. Tourism and hospitality management, 26(1), pp.173-193.
Rodriguez, A. and Smith, J., 2018. Phenomenology as a healthcare research method. Evidence-Based Nursing, 21(4), pp.96-98.
Sharma, M., 2017. Tourism Marketing in India: A Case Study. the land, 1, p.2.
statista.com, 2022. Annual change in the tourism revenue in China from 2010 to 2020, Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/236054/growth-rate-in-tourism-revenue-in-china/ [Accessed on: 15/01/2021]
tourism.gov.in, 2022. Tourism statistics, available at: https://tourism.gov.in/sites/default/files/2021-09/English%20Tourisum%202021.pdf [Accessed on: 15/01/2021]
Wang, L. and Wong, P.P.W., 2020. Marketing of environmentally friendly hotels in China through religious segmentation: a theory of planned behaviour approach. Tourism Review.
wttc.org, 2022. Economic Impact Reports, Available at: https://wttc.org/Research/Economic-Impact [Accessed on: 15/01/2021]



