Impact of acquisition and mergers on the economy of Australia
Abstract
This research has been based on the mergers or acquisitions that are taking place in Australia. With the help of secondary data and analysing them with Linear Regression and Correlation this research has been trying to find out its contribution towards the economy of Australia. This research has been able to find out the concepts that have been associated with these acquisitions and mergers and their importance in the Australian economy. Along with statistical data analysis this research has tried to bring out the probable contribution of these mergers and acquisitions that have been taking place recently in Australia.
This research explores mergers or acquisitions (M&A) in Australia. This research tries to find out the contribution of M&A
Acknowledgement
I express my gratitude and sincere thanks to the teachers, family members and my friends for their support and encouragement. I express my gratitude towards my mentor, without whom I would not have been able to conduct this research work. It is only with the guidance I have received from my mentor that I could understand the idea of research work and derive it in the form of this research work.
I would declare that the information as well as the data that I have shared in the form of this research are true to my knowledge. I have maintained all the research ethics which have been essential for this study. No confidential data were included in this research nor there have been any intend wrong interpretation of the ones that are presented.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6
1.1 Background……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
1.2 Aims……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
1.3 Objectives……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
1.5 Rationale……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
2. Literature Review…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7
Literature Gap……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 8
3. Methodology…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9
3.1 Research philosophy……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9
3.2 Research approach……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9
3.3 Data Collection……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9
3.4 Data analysis……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9
3.5 Research ethics……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10
4. Data Analysis……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11
4.1 Introduction……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11
4.2 The Perspective of Mergers and acquisitions……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11
4.3 Statistical Data Analysis……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12
5. Conclusion……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 16
5.1 Justifying Objective 1……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 16
5.2 Justifying Objective 2……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 16
5.3 Justifying Objective 3……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 16
List of References……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 18
List of Graphs
Graph 1: Difference in Revenue generated…………………………………………………………… 12
Graph 2: Difference in Assets…………………………………………………………………………….. 13
List of Tables
Table 1: List of Mergers and acquisitions selected for this research………………………… 11
List of Figures
Figure 1: Linear regression of revenue………………………………………………………………… 13
Figure 2: Linear Regression of Revenue……………………………………………………………… 14
Figure 3: Correlation with respect to assets………………………………………………………….. 14
Figure 4: Correlation with respect to Revenue………………………………………………..………..15
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
According to Ali, Salman and Khan, (2016) acquisitions and mergers have been an integral part of the legal procedure of a country which looks after the ways in which organisations can combine with one another for having a better economic sustainability in the long run. It is a system through which amalgamation of different organisations take place so that they can be able to derive a stable financial position in the market. In addition to this it also helps in reducing the threat from competitors by taking up mergers and acquisition. Moreover when two or more organisations merge with one another the try to look after the quality of product and services that are produced by these organisations. So, it enhances the type of services which can be offered to the customers.
Sarala, Vaara, and Junni (2019) also explained that it is through the merger and acquisition that cultural differences between organisations or a market can be overcome. It is a multi process where different types and forms of mergers and acquisitions can be performed by organisations. For example there are horizontal merger, vertical mergers cross border mergers and acquisitions.
Reddy and Xie, (2017) at present (verb missing) sustainability of energy is one of the most crucial factors which are being focused across different nations. It is through the proper coordination between organisations that sustainable use and production of energy resources can be developed. This is the reason why multinational organisations which are dealing in oil and gas industry have hundred different mergers and acquisitions since the year 1990 to present. These models for acquisitions and not just confined to the ones which are done by the country or within the country but it has spread to cross borders as well.
The three first paragraphs are clear and introduce well the problem. I have a small suggestion just in terms of style. You can be less formal in terms of references at this stage of the introduction. Instead of writing “article X states that Y is important”, you could turn it this way: “Y is important (see, e.g., article X)”. In terms of style, it suggests that you are writing down your thoughts supported by serious evidence, instead of simply mentioning a couple of papers.
If you have time, there is room for you to give a more personal tone at the beginning of the introduction.
1.2 Aims (In the introduction, we usually do not show the structure in terms of sections. The idea is that, if your introduction is well written, the reader can understand everything by themselves)
This research aims at finding out the impact of acquisitions and mergers on the organisations that are based in Australia and thereby their contribution towards the economy.
1.3 Objectives
The objectives of this paper are as follows:
- To find the influence of synergy due to addition of acquired assets
- To investigate synergies of acquisition with respect to other options
- To recommend synergy measurement for acquisition
1.5 Rationale
This study has rights to ascertain the role of mergers and acquisitions for enhancing the financial condition of an organisation and thereby their role in the economy. This is help in finding out the influence of acquisitions and mergers on the economic development of Australia.
Here, you can briefly present the statistical method(s) your are using, and you can write the main results from the data analysis.
2. Literature Review
According to Loyeung, (2019) when it comes to financial mergers and acquisitions organisations try to develop strategies through which we can benefit the target group of customers I am getting involved with such these which will help them to enhance their values and never better seduction for teacher in the market. It is with the help of mergers and acquisitions that organisations can be able to derive accumulative return from the industry at a quite higher rate. In most of the cases is a financial advisor or a team of advisors who was selected for describing the underlined situation and taking off required decision related to mergers and acquisitions. It is true the first merger performance that the impact of merger and acquisition on an organisation can be derived.
Social situations like financial crisis or global crisis there are a number of strategies which may not work appropriately (Bakir, 2019). In such cases it is the organisations dealing in banking sector which undergo mergers and acquisition for dealing with the crisis. There are different types of mergers and acquisitions taking place all over the world with the regulations and policies which are being reinforced for financial stability of organisations industry and the country as a whole. It can also be explained the Australia has more regulations and policies through which it can reach towards better management of crisis situation by involving mergers and acquisition in its system. It is not just the size of the assets but it is also the interconnection between different banking organisations and their internationalisation which helps to develop a stable financial condition and fight with different hostile tribes which may arise in the industry.
In case of international corporate governance cross border mergers and acquisitions is an integral part for both social and financial improvement (Albuquerque, 2019). This helps the ultimate development of social and financial structures giving rise to identification of global markets and accessing them irrespective of the cultural similarities and dissimilarities. So these acquisitions and mergers and not just confined with the development of any particular organisation but it has spread over the national and international levels and have a significant impact on the economy of the countries involved.
While considering mergers and acquisitions it is not just the positive impact which should be considered for overall analysing of its influence what it is also the negative ones which should be kept in mind (Lee, 2018). For example there is political uncertainty which is associated with these acquisitions of mergers taking place in the country especially in case of cross-border acquisitions. While following cross-border acquisitions organisation tends to have a mutual benefit but there can be instances where one organisation may get more benefits than the other. In such cases if two or more nations are involved it becomes difficult to understand the impact of this merger or acquisition or a particular country. This is the reason why considering cross border mergers and acquisitions may make it difficult to understand their exact impact on the country on its economy because there are other countries that are also associated with this venture. Yet for taking into account the global perspective and the sustainability of organisation of the industry, amidst the political uncertainty, cross border mergers and acquisitions are still into play in different parts of the vault involving a number of countries.
In the opinion of Degbey et al, (2020) there are some other factors which are also required to be considered while implementing mergers and acquisition in any industry. The primary factor is the employees who are an integral part of an organisation. For ensuring proper employee motivation in upcoming future it is also necessary for organisations not to overlook the role of the employees. This will not only help them to estimate the number of employees would be a part of this mulched organisation or acquired organisation but will also help them to ensure that there is effective use of Human resource Management policies for the new amalgamated setup. Mergers are also possible in academic fields like merges of different universities which can help to develop a new drive in the field of mergers and acquisition taking into consideration the growth of global scenarios (Sułkowski, Seliga, and Woźniak et al, 2019).
A market can function at its best when there is traffic competition along with taking care of the supply and demand. Now if market faces Monopoly then it can have a negative impact on the economy of the country this is the reason why before the establishment of an acquisition and merger in Australia the feasibility and chances of monopoly establish thereafter are analysed. According to Takeovers, (2020) there is a panel of peer reviewed bodies which look after the transactions taking place between corporate and Australian entities especially in case of mergers and acquisitions. This is the reason why if there are any disputes in the resolution which is against the economy of the country and public interest it takes required action.
Acquisition
The terminology acquisition is known as a corporate special behaviour along with actions for taking over other business. The objective of acquisition is to increase the business by means of volume, market share, enhancing opportunity in other technology or product lines, decreasing cost of materials, exploring new geography and many more. The theoretical version of acquisition actually defines the opportunity for the acquirer as the synergy from different aspects. In this context, many large and small companies either merge of acquire small firms with different objectives. The acquisition helps to grow a business faster along with utilise idle cash to explore for new ventures.
Merger and acquisition in Australian context
The M&A activity in Australia has shown robust growth recently as compared to 2008. The current volume of large M&A is accounted for 583 numbers of deal just few percentage below of 2017’s record of 618. In 2008, the country witnessed M&A activity at large scale of 375 deals only (Dealtracker 2019, 2020). Moreover, the current deal of M&A activity has recorded value of $88.5 billion in 2018 surpassing the record of 2017 of $85.6 billion. The mid-market M&A has witnessed 70% of total deal whereas large cap deal is made of 16% of total M&A activities (Dealmakers:Mid-market M&A in Australia 2019, 2020). Total number of M&A deal in the country has recorded 1909 deals including all types of M&A deals. The corporates have remained the largest acquirer by volume as 91% deals are signed by them in the last 18 months (Australia M&A and PE activity hits new heights in 2018 | Lexology, 2020). Till date the domestic buyers have contributed the much needed money in M&A as 31% value of M&A has come from international transactions.
Literature Gap
The past studies have focused on various measurement of synergies from financial aspects. The acquired assets of the business enhances the opportunity of the new or expanded firms to increase its revenue. However, the previous studies lack of clarification about the influence of total assets over the revenue after acquisition. The change can be observed post-acquisition in revenue due to changing in assets of the acquired firm. Hence, the literature gap is generated here as the synergy generated from acquired asset and others, which creates the current hypothesis for this study (M&A Statistics by Countries – Institute for Mergers, Acquisitions and Alliances (IMAA), 2020).
Hypothesis:
Post-acquisition, only total assets have positive influence on the revenue of the acquiring company
3. Methodology
This research has been based on a few steps which can be determined to be the methodology of this research work. It is not just a framework on which the research has been established but this is also a guideline which has been followed to derive the research results (Mohajan, 2018).
3.1 Research philosophy
Positivism is a research philosophy which helps students to determine the research results in a more scientific manner (Edson, Henning and Sankaran, 2016). Moreover the variables are interpreted in terms of their behaviour without interfering with it. So, positivism has been chosen as a form of research philosophy for this research work.
other research philosophy like interpretivism, realism and pragmatism focus more on the behaviour of the variables than that of the ways in which the variables could have influencing to research phenomenon. So positivism has been more appropriate for this research.
This research is based on the deductive approach (Opie, 2019). It is with the help of reactive approach that a researcher can be able to consider existing literatures and further compare them with the collected data for deriving better research results.
this research has taking into account mergers and acquisitions a deductive research approaches helps to determine the scenarios highlighted by existing literature and thereby analysing in the present scenario with respect to the secondary data collected during this research work.
3.2 Sampling method and data analysis
There are lots of M&A activities have been done in 2018. However, the listed companies in Australia are selected for this sample whereas the target of the acquired firms of the deal. The merger deal, unlisted deals, small cap, specific mid-market deals acquired by foreign bidders, acquisition by government bodies and foreign fund managers investment for acquiring Australian companies are not selected for this sample. Moreover, foreign companies acquiring foreign assets of Australian companies (separate entity or subsidiary) is consider here as sample. It is been tried to avoid such acquirer to investigate in the research, which have acquired multiple companies during the period. In this way, the true sense of acquisition and its impact can be measured after acquiring a company (Onwuegbuzie and Collins, 2007). Therefore, the sampling method can be construed as stratification of acquired firms on basis of type of deal and acquiring firm’s status and few others.
Secondary data is conducted for this study as total assets and revenue of the acquired firm are collected from past financial performance. Further, the data analysis has ensured to describe the statistics for 4 financial from the perspective of all acquirer firms. The inferential analysis is conducted by using correlation and regression test. The regression test has ensured to prepare the predictive model for forecasting revenue of acquirer with respect to total assets after acquisition.
3.3 Data Collection
For the collection of data this research has been based on mainly secondary data considering the financial position of organisations before and after they have undergone acquisitions or mergers in Australia (Johnston, 2017). Variables like the revenue generated by the organisation and its total assets have been considered to be factors for deriving the research results. Four instances of acquisitions or mergers have been chosen consisting of 8 organisations in order to collect secondary data for this research work.
Justification after taking into account the vast domain of the research work secondary research has been more appropriate because it has helps to analyse the financial and economic implications of acquisitions and merger with respect to the present day organisations. Secondary data has been derived from annual report of the organisation which is authentic in nature and helps to collect more data within this limited period of time.
3.4 Data analysis
For the analysis of financial data consisting of the revenue and asset of the organisations there were different tables and charts which were used as a form of data analysis methods. Along with this statistical analysis tool like linear regression and correlation has been used to estimate the final result of this research work (Syazali et al, 2019).
Justification: with the use of statistical has helped to derive accurate research results understand the actual growth of organisations with respect to their mergers and acquisitions done in the recent years.
Research model
Total assets of the acquired firm influences the revenue post-acquisition is the main objective of this study. Hence, the model of study has decided to conduct a correlation test among the average total assets and revenue of the acquirer firms (average) for total period of 4 years. In this context, all the firms’ revenue and total assets are collected for four years (1 year of post-acquisition). The average of revenue and total assets are undergone correlation test for understanding the relationship between increasing total assets by acquisition on revenue. Further, the acquirer firm’s revenue is predicted along with the assets through regression analysis. In this context, total assets is independent variable that is used as influencing element of revenue.
Revenue = constant + coefficient * total assets
The regression test allow the researcher to find the influence of the total assets on the revenue along with impact as synergy on acquirer. The research hypothesis can be tested through measuring the influence of assets over revenue generation.
3.5 Research ethics
All the research ethics like honesty confidentiality integrity has been thoroughly maintained during the course of the research work. No confidential data have been accessed in the form of secondary data collection. There has been honest interpretation of data using statistical tools and at the same time considering honesty and integrity while interpreting these data.
4. Data Analysis
4.1 Data Source
The data analysis has been based on the following organizations which have recently undergone merger or acquisition in Australia.
| Target company | Acquirer | Year of acquisition |
| DXC Technology | Luxoft | 2018 |
| Unibail-Rodamco-Westfield | Westfield Corporation | 2017 |
| Tabcorp Holdings Limited ( | Tatts Group Limited | 2018 |
| Yancoal Australia Ltd ( | Coal & Allied Industries Ltd | 2018 |
| Nine Entertainment Co. Holdings Limited | Fairfax Media Limited | 2018 |
| Santos | Quadrant Energy | 2018 |
Table 1: List of Mergers and acquisitions selected for this research
(Source: Author)
| Revenue | ||||||
| DXC Technology | Unibail-Rodamco-Westfield | Tabcorp Holdings Limited ( | Yancoal Australia Ltd ( | Nine Entertainment Co. Holdings Limited | Santos | |
| FY16 | 7106 | 1122.6 | 2188.7 | 1238 | 1286 | 2594 |
| FY17 | 7607 | 1419.5 | 2234.1 | 2601 | 1244 | 3107 |
| FY18 | 21733 | 1985.5 | 3764.7 | 4850 | 1403 | 3660 |
| FY19 | 20753 | 2125.2 | 5482.3 | 4460 | 1965 | 4033 |
| Total assets | ||||||
| DXC Technology | Unibail-Rodamco-Westfield | Tabcorp Holdings Limited ( | Yancoal Australia Ltd ( | Nine Entertainment Co. Holdings Limited | Santos | |
| FY16 | 7736 | 18765.5 | 3302.8 | 7660 | 2148 | 15262 |
| FY17 | 8663 | 21254.3 | 3740.9 | 12313 | 1901 | 13706 |
| FY18 | 33921 | 64257.2 | 12940.8 | 11379 | 1853 | 3660 |
| FY19 | 29574 | 65003.2 | 13299.1 | 11093 | 4409 | 4033 |
Table 2: Financial Position of the Organisations before and after acquisition or mergers
(Source: M&A Statistics by Countries – Institute for Mergers, Acquisitions and Alliances (IMAA), 2020)
Table 2 describes the amount of revenue generated by the organisation before and after its merger and acquisition. In addition to this the total asset of the organisation before and after acquisition or merger has also been represented in this table. Table 2 should go in the previous subsection where you are presenting the data. You could try to merge tables 1 and 2 to save space.
It is important to define the variables. How is the revenue defined? And total asset? What do they capture economically? Do they capture the same thing?
For example, for cases 1 and 2. Case 1 shows large total asset and relatively small revenue. Case 2 shows the reverse. What does it mean for these firms? Is there one measure that is better than the other to capture performance?
Also, there is a level effect. It would be useful to see the change in %. For instance, case 4 shows an increase in revenue of 300, which is not much compared to the level of revenue for Vodafone. However, this may by large % increase. Consider using growth rate.
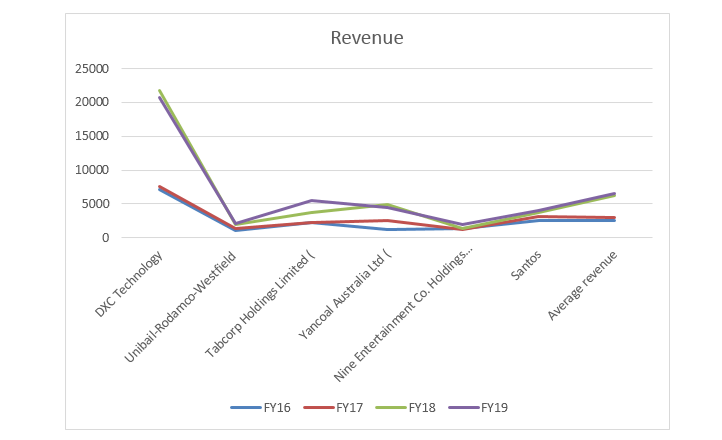
Graph 1: Difference in Revenue generated
(Source: Author)
This graph clearly denotes that there has been increase in the revenue generated by the organisation after acquisition or merger in certain instances. On the other hand for other instances ever decrease in the revenue generated by the organisations after their acquisition or mergers.
Total change in revenue of post-acquisition can be observed for the individual acquirer in the above figure where the change in revenue and before acquisition can be observed clearly. There are some companies have performed well post-acquisition as revenue has multifolded by many times. The average revenue is observed to be increased in 2018-19 due to acquisition of new firms.
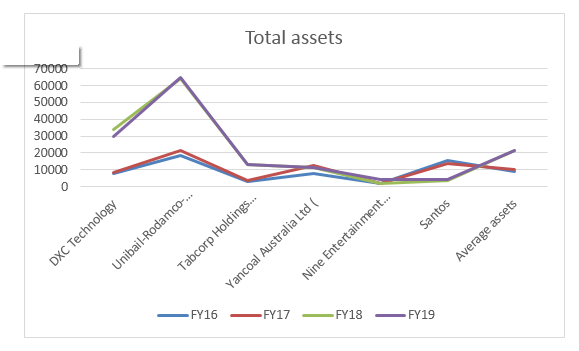
Graph 2: Difference in Assets
(Source: Author)
The above figure shows the total assets before and after acquisition of new firms. The average assets of the companies have increased for some of the companies did not show much increase in total assets. Further, some companies have generated huge assets post-acquisition indicating large acquisition is placed under the deal.
Similar to revenue in case of the total asset of the organisations it can be noted that in certain instances there were increase in the total asset hold by the organisation before its merger or acquisition while in other cases there was a decrease in the total assets of the organisation after their merger and acquisition. So it can be explained from these graphs that both revenue and asset can be e better generated after acquisition and merger in certain cases but subsequently there can also be decrease in these amounts. Acquisition and merger can lead to words in answering the financial growth of the organisation again in certain cases it can lead to the decrease in the financial performance of the organisation.
Correlation
| Revenue | Total assets | |
| Column 1 | 1 | |
| Column 2 | 0.998367 | 1 |
Table 3: Correlation matrix
The high correlation between total assets and revenue indicates that influence of total assets is high on revenue. However, correlation test lacks of indicating the specific reasons of influencing revenue with different perspectives. Moreover, misinterpretation of data for different figures may affect correlation test.
Regression analysis
| Regression Statistics | ||||||||
| Multiple R | 0.998 | |||||||
| R Square | 0.997 | |||||||
| Adjusted R Square | 0.995 | |||||||
| Standard Error | 143.662 | |||||||
| Observations | 4 | |||||||
| ANOVA | ||||||||
| df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | ||||
| Regression | 1 | 12610186.53 | 12610186.53 | 610.99 | 0.00 | |||
| Residual | 2 | 41277.69 | 20638.84 | |||||
| Total | 3 | 12651464.22 | ||||||
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | |
| Intercept | -158.36 | 204.78 | -0.77 | 0.52 | -1039.45 | 722.73 | -1039.45 | 722.73 |
| Total assets | 0.31 | 0.01 | 24.72 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.36 |
Table 4: Linear Regression of Revenue
(Source: Author)
The F test indicates that the result is significant to understand the relationship between total assets and revenue. The regression test result indicates that only 0.31 parts of total assets have influence over the revenue post-acquisition. The regression equation becomes
(Y) Revenue = -158.36 + 0.31* X1 (total assets)
Therefore, the hypothesis cannot be acceptable as only 31% of revenue increase post-acquisition can be explained by total assets of the acquirer. The synergies generated in other form by the deal of acquisition requires to be tested further as the hypothesis of this study is failed to provide positive direction.
The revenue function Y is function of total assets. This means the revenue of the firm is depending on the total assets of the firm. This is one-one relationship and is positively related. This means 1% increase in one variable will increase another variable by 1%.
So, from the results of linear regression statistics and correlation it can be noted that even though there is variation in the generation of revenue and the total number of assets sometimes being positive and sometimes be negative, they are positively correlated with each other. It can be interpreted from this analysis that even though at times there is less revenue or asset generated by an organisation after merger or acquisition yet there is a positive correlation ship between the financial performances. If an organisation has a stable financial performance before its merger and acquisition it will continue to have the same in most of the cases. There can be initially issues faced by the organisation when dealing with internal or external factors after the merger and acquisition yet there would be a consistency in the behaviour of the organisations in terms of the financial performances.
5. Conclusion
This conclusion has been drawn with respect to the objectives which have been setup for this research.
5.1 Justifying Objective 1
To find out the importance of acquisitions and mergers among the organisations dealing in Australia
From this research it was found that in Australia acquisitions or mergers are done among organisations for initiating organisational sustainability and at the same time reducing the rate of competition from other organisations. In addition to this there are some other factors like financial crisis a global crisis where different organisations and banks may tend to merge with each other for providing the customers with better facilities and services. At times there can also be competitions from the giants of a market or industry which can make it difficult for other organisations to cope up with the scenario. This is the reason why organisation spends too much with each other for generating better sustainability in the long run. Acquisitions are done by organisations which are comparatively larger so that they can take skilled employees or software that has been used by the smaller organisations by acquiring them and become a joint in the industry itself. Yet in order to avoid Monopoly there are different rules which are set up by the government for ensuring healthy competition and regulating acquisitions and mergers accordingly.
5.2 Justifying Objective 2
To identify the impact of acquisition and mergers on the organisations dealing in Australia and the economy of the country
From the secondary data analysis it has been understood that in order to have achieving financial position in the market and organisation is required to have effective generation of revenue and assets before initiating any mergers or acquisition. This is mainly because there is a correlation between the amount of revenue or assets of an organisation present before the merger and acquisition and after the merger and acquisition. So beautiful this relation organisations are required to consider their existing performances in order to enhance their performance after merger and acquisition. Yet in certain cases even after mergers and acquisitions completed organisations can face a downfall in the generation of revenue or their assets due to the change in their business environment both internally and externally. Suits required being considerate of both positive and negative issues which may come of interview of acquisition and mergers conducted organisations in Australia and their why impact its economy subsequently.
5.3 Justifying Objective 3
To recommend strategies through which acquisitions and mergers can contribute towards the organisations and thereby developing the economy of Australia.
- From this research it can be recommended that organisations are required to consider both the positive and negative aspects of acquisitions and mergers before conducting it.
- It is also necessary for organisations to consider their existing financial position like there capable of generating revenue and their assets in hand so that they can consider required steps for the implementation of acquisition or mergers in the country.
List of References
Albuquerque, R., Brandão-Marques, L., Ferreira, M.A. and Matos, P., 2019. International corporate governance spillovers: Evidence from cross-border mergers and acquisitions. The Review of Financial Studies, 32(2), pp.738-770.
Ali, H.A.M., Salman, M.J. and Khan, M.A., 2016. A GLANCE AT TAKEOVER MODELS IN AUSTRALIA, MALAYSIA, SINGAPORE AND THE UNITED KINGDOM. Journal of Asian and African Social Science and Humanities, 2(3), pp.31-46.
Australian Financial Review, 2020. The Next Big Question For TPG And Vodafone’s Mega-Merger. [online] Australian Financial Review. Available at: <https://www.afr.com/chanticleer/the-next-big-question-for-tpg-and-vodafone-s-mega-merger-20200624-p555td> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Bakir, C., 2019. How do mega-bank merger policy and regulations contribute to financial stability? Evidence from Australia and Canada. Journal of Economic Policy Reform, 22(1), pp.1-15.
CRN Australia, 2020. 2019’S Biggest Mergers And Acquisitions… So Far. [online] CRN Australia. Available at: <https://www.crn.com.au/gallery/2019s-biggest-mergers-and-acquisitions-so-far-526639> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Degbey, W.Y., Rodgers, P., Kromah, M.D. and Weber, Y., 2020. The impact of psychological ownership on employee retention in mergers and acquisitions. Human Resource Management Review, p.100745.
Deloitte, 2020. [online] Www2.deloitte.com. Available at: <https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/au/Documents/finance/insolvency/mf-global/meetings-and-reports/deloitte-au-fas-mfga-annual-report-2018-210918.pdf> [Accessed 13 July 2020].
DXC Technology, 2020. [online] Assets1.dxc.technology. Available at: <https://assets1.dxc.technology/investor_relations/downloads/MD_7743a-19_Annual_Report_2018_10-K_v34.pdf> [Accessed 13 July 2020].
DXC Technology, 2020. DXC Technology Completes Acquisition Of Leading Digital Innovator Luxoft. [online] DXC Technology. Available at: <https://www.dxc.technology/newsroom/press_releases/146800-dxc_technology_completes_acquisition_of_leading_digital_innovator_luxoft> [Accessed 13 July 2020].
Edson, M.C., Henning, P.B. and Sankaran, S. eds., 2016. A guide to systems research: Philosophy, processes and practice (Vol. 10). Springer.
Johnston, M.P., 2017. Secondary data analysis: A method of which the time has come. Qualitative and quantitative methods in libraries, 3(3), pp.619-626.
Lee, K.H., 2018. Cross‐border mergers and acquisitions amid political uncertainty: A bargaining perspective. Strategic Management Journal, 39(11), pp.2992-3005.
Loyeung, A., 2019. The role of boutique financial advisors in mergers and acquisitions. Australian Journal of Management, 44(2), pp.212-247.
Mohajan, H.K., 2018. Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 7(1), pp.23-48.
Opie, C., 2019. Research approaches. Getting Started in Your Educational Research: Design, Data Production and Analysis, p.137.
Powernet, 2018. [online] Powernet.co.nz. Available at: <https://powernet.co.nz/uploads/2018/06/2018_PNL_AnnualReport_WEB_22Jun.pdf> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Powernet, 2019. [online] Powernet.co.nz. Available at: <https://powernet.co.nz/uploads/2019/06/PNL-AnnualReport2019-Webready.pdf> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Reddy, K.S. and Xie, E., 2017. Cross-border mergers and acquisitions by oil and gas multinational enterprises: Geography-based view of energy strategy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, pp.961-980.
Reuters, 2020. Australia Court Approves $10 Billion Vodafone-TPG Merger, Overrules Regulator. [online] U.S. Available at: <https://www.reuters.com/article/us-vodafone-group-m-a-tpg-telecom/australia-court-approves-10-billion-vodafone-tpg-merger-overrules-regulator-idUSKBN20634O> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Sarala, R.M., Vaara, E. and Junni, P., 2019. Beyond merger syndrome and cultural differences: New avenues for research on the “human side” of global mergers and acquisitions (M&As). Journal of World Business, 54(4), pp.307-321.
Sułkowski, Ł., Seliga, R. and Woźniak, A., 2019. Strategic challenges of mergers and acquisitions in the higher education sector. Entrepreneurial Business and Economics Review (EBER), 7(2).
Syazali, M., Putra, F., Rinaldi, A., Utami, L., Widayanti, W., Umam, R. and Jermsittiparsert, K., 2019. Partial correlation analysis using multiple linear regression: Impact on business environment of digital marketing interest in the era of industrial revolution 4.0. Management Science Letters, 9(11), pp.1875-1886.
Takeovers, 2020. The Takeovers Panel. [online] Takeovers.gov.au. Available at: <http://www.takeovers.gov.au/> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
The Guardian, 2020. Vodafone And TPG $15Bn Merger Given Green Light By Federal Court. [online] the Guardian. Available at: <https://www.theguardian.com/business/2020/feb/13/vodafone-and-tpg-15bn-merger-given-green-light-by-federal-court> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Vodafone, 2019. [online] Media.corporate-ir.net. Available at: <http://media.corporate-ir.net/media_files/IROL/77/77862/annual-reports/annual_report19/downloads/Vodafone-full-annual-report-2019.pdf> [Accessed 26 June 2020].
Vodafone, 2020. [online] Investors.vodafone.com. Available at: <https://investors.vodafone.com/static-files/947ac784-3257-42e4-a543-ad7c5ea31d0e> [Accessed 26 June 2020].






